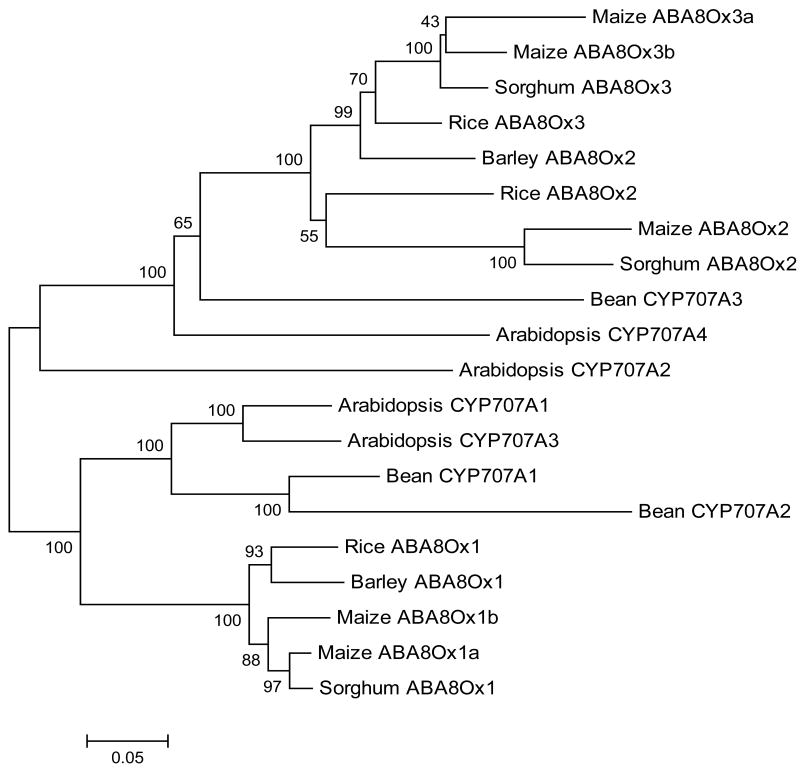
Fig. 3.
Phylogenetic analysis of proteins encoded by members of the CYP707A gene subfamily for representative monocots and dicots. A neighbor-joining tree was constructed using the following protein sequences (given as accession numbers): Zea mays (ABA8Ox1a, DR806072; ABA8Ox1b, CD433445; ABA8Ox2, CO460095; ABA8Ox3a, EC904849; ABA8Ox3b, CD941324), Oryza sativa (ABA8Ox1, LOC_Os02g47470; ABA8Ox2, LOC_Os08g36860; ABA8Ox3, LOC_Os09g28390), Sorghum bicolor (ABA8Ox1, Sb04g030660; ABA8Ox2, Sb07g022990; ABA8Ox3, Sb02g026600), Hordeum vulgare (ABA8Ox1, DQ145930; ABA8Ox2, DQ145931), Arabidopsis thaliana (CYP707A1, At4g19230; CYP707A2, At2g29090; CYP707A3, At5g45340; CYP707A4, At3g19270), Phaseolus vulgaris (CYP707A1, DQ352541; CYP707A2, DQ352542; CYP707A3, DQ352543). Amino acid distances were subjected to Poisson correction. Numbers indicate bootstrap support for individual nodes. Bootstrap support higher than 40% is indicated at respective nodes (n = 500).