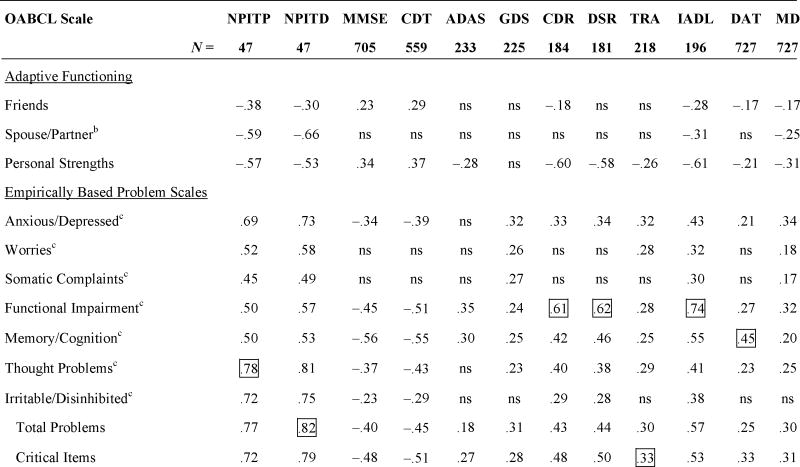
TABLE 2.
Largest Bivariate Correlations Between OABCL Scale Scores and Each Other Index of Functioninga
 |
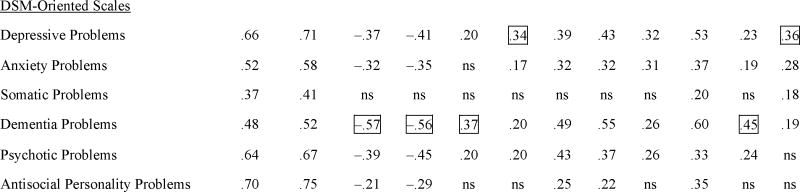 |
Boxes indicate the strongest association of an OABCL scale with each other index; ns = correlations that were p>.05 after correction of alpha for the number of analyses (Sakoda et al., 1954).
NPI = Neuropsychiatric Inventory Total Problems (TP) and Total Distress (TD) caused by subject’s problems; MMSE = Mini-Mental State Examination; CDT = Clock Drawing Test; ADAS = Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognitive Subscale; GDS = Geriatric Depression Scale; CDR = Clinical Dementia Rating; DSR = Dementia Severity Rating; TRA = Trail Making Test Part A; IADL = Instrumental Activities of Daily Living; DAT = Dementia of the Alzheimer’s type; MD = Mood disorder. All indices were based on direct assessments of subjects’ functioning except the NPI, which is a clinical interview of informants, and the IADL, which was completed by collaterals.
N who had lived with spouse/partner in the preceding 2 months ranged from 23 for the NPI to 313 for the diagnoses.
Factor-analytically derived syndrome scales.
