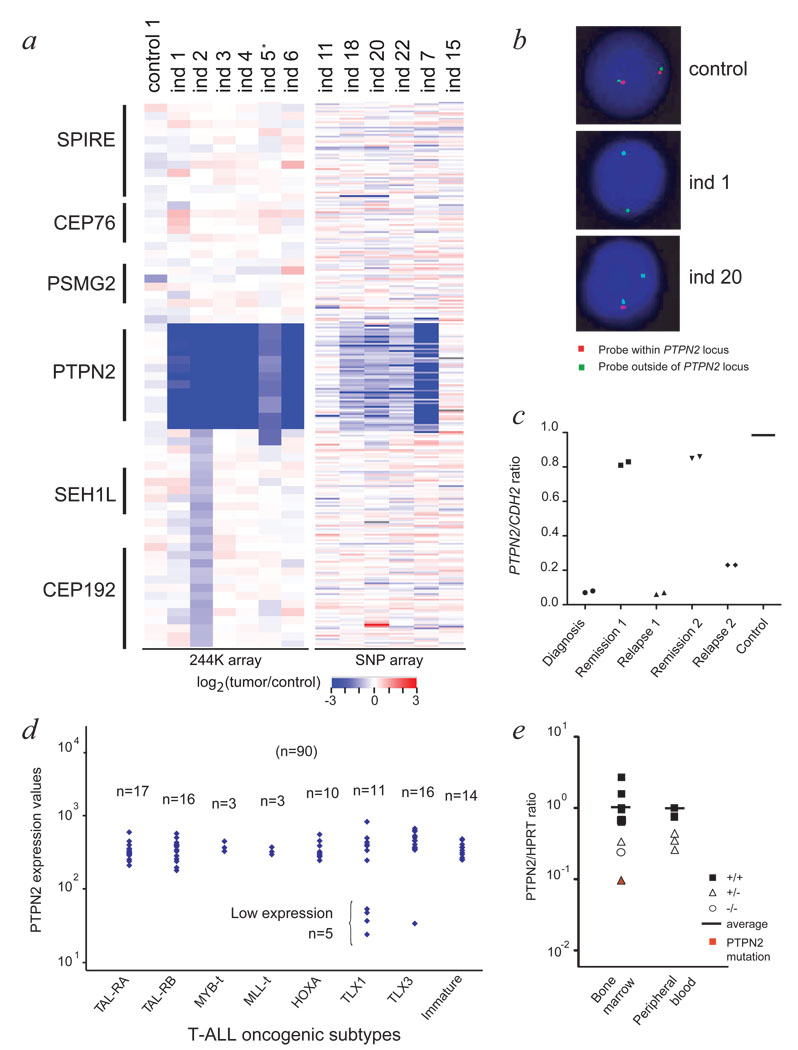
Agilent array CGH and Affymetrix SNP array data for 13 T-ALL cases indicating bi-allelic deletion of PTPN2 in individuals 1 to 7, and mono-allelic deletion of PTPN2 in individuals 18, 20 and 22. *blast cell content for individual 5 was only 50%.
Interphase fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) confirmed the presence of PTPN2 deletion in >90% of the cells for individuals 1 (bi-allelic deletion) and 20 (mono-allelic deletion).
Quantitative PCR analysis on genomic DNA isolated from diagnosis, remission and relapse samples of individual 1 confirmed that the deletion was acquired at diagnosis, and again present at relapse. A primer set for CDH2 (18q12) was used for normalization.
PTPN2 expression level was analyzed in a T-ALL patient set (n=90) using Affymetrix gene expression arrays (probeset 213136_at) and categorized according to oncogenic T-ALL subtypes (x-axis). Y-axis displays PTPN2 expression levels as a logarithmic scale. N indicates number of patients analyzed.
Quantitative real-time PCR analysis of T-ALL patients detects lower expression levels for T-ALL cases with loss of PTPN2 compared to T-ALL patients with no deletion. Expression values were normalized for HPRT gene expression and blotted at the y-axis in logarithmic scale. Samples derived from bone marrow or peripheral blood were analyzed separately. Closed rectangles: no deletion (n=8); open triangles: mono-allelic deletion (n=5); open circle: bi-allelic deletion (ind 1). The individual with an additional mutation in PTPN2 is shown in red.