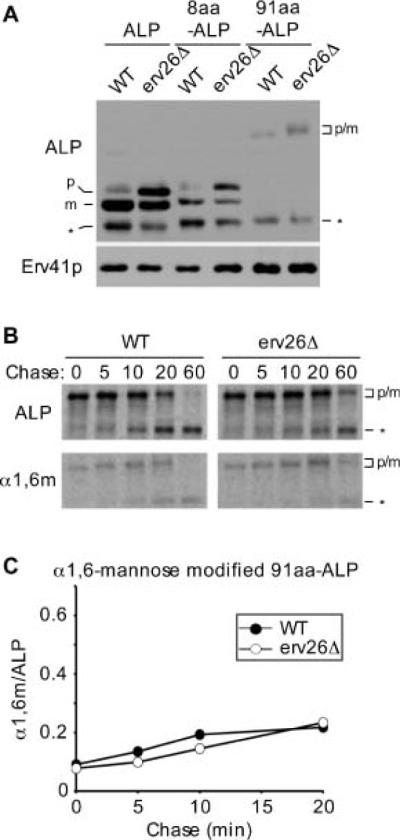
Figure 7.
The position of pro-ALPs lumenal domain from the inner ER membrane influences Erv26p-dependent export. A) Wild-type (CBY2151) and erv26Δ (CBY2240) cells expressing either full-length pro-ALP (pFL8), the 8 amino acid insertion (pEC5) or the 91 amino acid insertion construct (pQC72) were converted to spheroplasts and proteins detected by immunoblot. The pro-ALP (p), mature ALP (m) and a soluble breakdown product (*) are indicated. B) Pulse-chase analysis of the 91aa-ALP protein in wild-type and erv26Δ strains expressing pQC72. C) Graphical depiction of the results in (B) plotting α1,6-mannose modified 91aa-ALP protein divided by total 91aa-ALP at the start of the time–course.