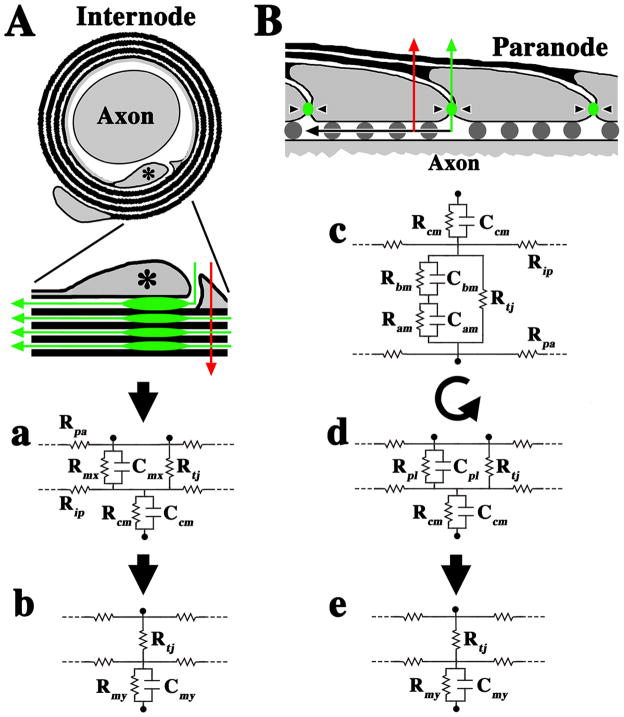
Fig. 8. Morphological model and equivalent circuits to describe the TJM.
A. Cross-section of a myelinated internode showing compact membrane (black) overlying an inner mesaxon (asterisk). The expanded view shows a trans-myelin pathway (red) across the compact membrane layers (red arrow) and a spiral pathway across the TJs. The TJs are aligned in the myelin but do not form a transverse current pathway. Rather, the flow is spiral through the TJs, which are in series with each other in successive myelin wraps and form a spiral pathway through the intramyelinic space. a. An equivalent circuit for the non-compact inner loop “microepithelium” (upper portion) and the compact membrane stack (lower). Rpa, axial periaxonal resistance; Rip, axial lamellar resistance. Rmx, Cmx, resistance and capacitance of the mesaxonal membrane; Rcm and Ccm, the resistance and capacitance of the myelin; Rtj, TJ resistance. The TJ capacitance is assumed to be negligible compared to the membrane capacitance (Clausen, 1989; Reuss, 2001) and is ignored. b. Because the mesaxonal/paranodal membrane resistance is high (Chiu and Schwarz, 1987), transverse currents may be largely shunted through Rtj, and the circuit can be simplified by placing Rtj in series with the myelin resistance and capacitance, Rmy and Cmy. B. Longitudinal section of a paranode (gray) and overlying myelin lamellae (black). Red and green arrows represent trans-myelin and spiral TJ pathways, respectively. Black arrow represents axial pathways through the periaxonal space, which is partially filled with axoglial junctions (dark gray circles). c. The equivalent circuit of paranodal loops shows compact myelin membranes (upper portion) and the paranodal loop “microepithelium” (lower). Ram, Cam, resistance and capacitance of the apical membrane of the paranodal loops; Rbm, Cbm, the basal membrane. d. Partial simplification of the circuit, where Ram, Cam and Rbm, Cbm are combined to yield Rpl, Cpl and the circuit is rotated 180° for comparison with the circuit in Aa. e. Similar to Ab, the circuit in Bd is simplified.