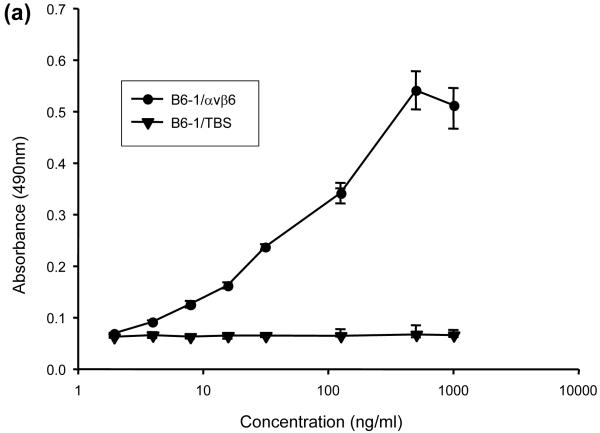
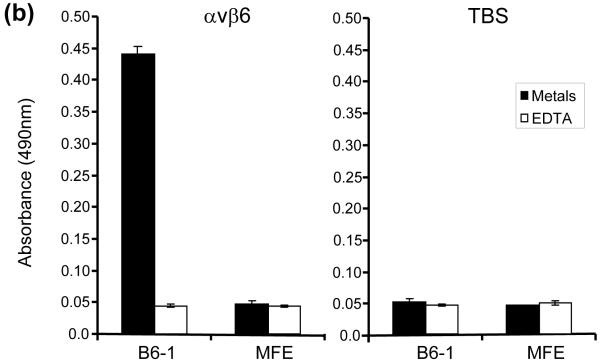
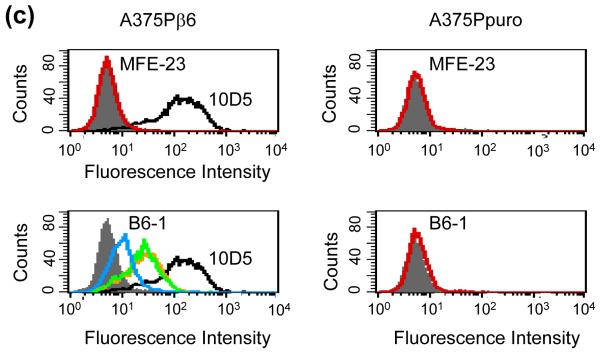
Fig. 2.
Interactions of B6-1 with αvβ6. (a) Graph showing concentration-dependent binding of B6-1 to immobilized αvβ6 in ELISA. B6-1 (various concentrations) was applied to immobilized αvβ6 or control Tris-buffered (TBS) wells. Binding was detected with rabbit anti-MFE-23 IgG followed by goat HRP-linked secondary anti-rabbit IgG antibody. (b) Graph showing cation-dependent binding of B6-1 to immobilized αvβ6 in ELISA. B6-1 or MFE (both at 0.5 μg/ml) was applied to immobilized αvβ6 or control Tris-buffered (TBS) wells either in the presence of Ca2+, Mg2+ and Mn2+ (cations) or in the presence of EDTA (5 mM). Binding was detected as described in (a). (c) Flow cytometry analyses show concentration-dependent binding of B6-1 to αvβ6 on cells. MFE-23 or B6-1 was allowed to bind to αvβ6-expressing (A375Pβ6) and non-expressing (A375Ppuro) cells. 10D5 murine anti-αvβ6, used at 10 μg/ml as a positive control for β6-transfected cells, is shown in black in both left panels. Bound scFvs were detected with mouse anti-Tetra-His IgG followed by Alexa Fluor 488®-conjugated anti-mouse IgG. Top left panel shows A375Pβ6, and top right panel shows A375Ppuro cells and MFE-23 at 50 μg/ml (red); bottom left panel shows A375Pβ6 cells and B6-1 at 5 μg/ml (orange), 0.5 μg/ml (green) and 0.05 μg/ml (blue). The 50 μg/ml concentration (not shown) had a shift in fluorescence intensity identical with that for the 5 μg/ml concentration; bottom right panel shows A375Ppuro cells, B6-1 at 50 μg/ml (red). Cells treated with mouse anti-Tetra-His IgG and Alexa Fluor488®-conjugated anti-mouse IgG only (omission controls) are shown in grey. The data represent the mean of triplicate measurements, and error bars represent the standard deviation at each data point (a and b).