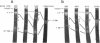Abstract
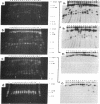
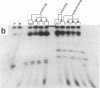
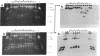
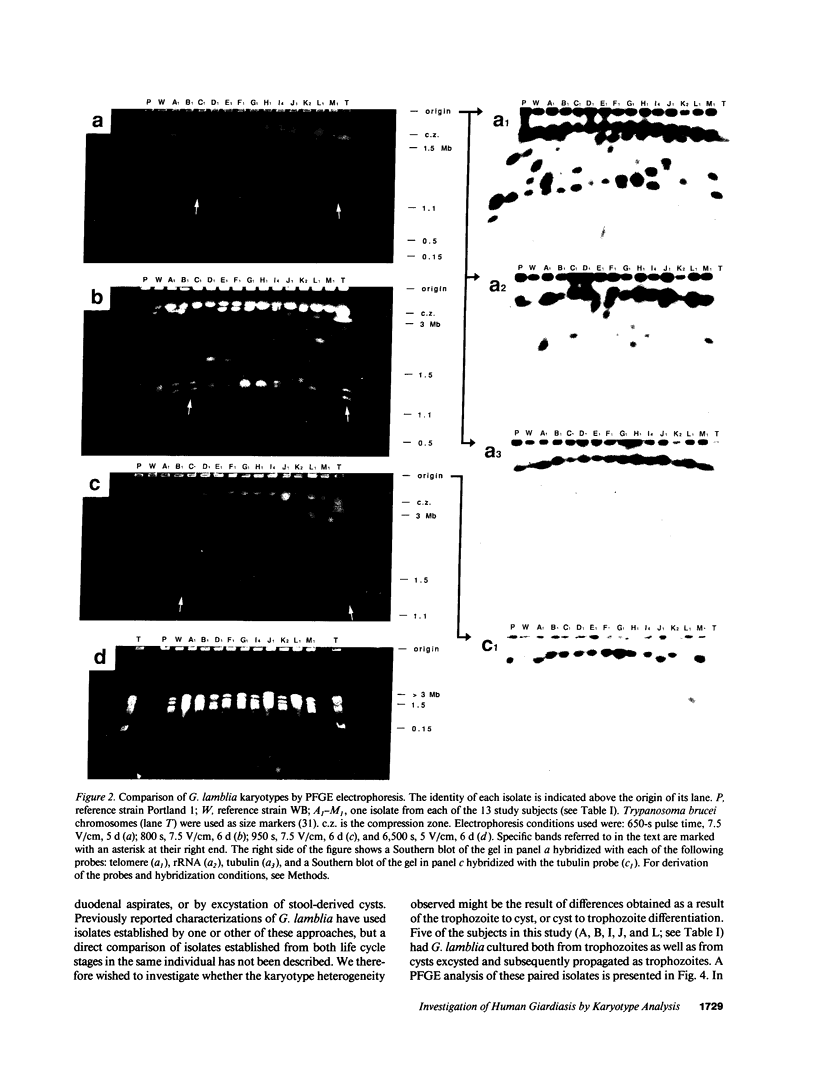
The patterns of transmission of Giardia lamblia and the potential contribution of strain differences to pathogenicity of infection is poorly understood. We used pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis (PFGE) to separate chromosome-sized DNA molecules of 22 stocks of G. lamblia isolated from 13 individuals (6 symptomatic, 7 asymptomatic) living in Jerusalem. PGFE gels run under a variety of conditions revealed up to nine ethidium bromide-stained bands per isolate ranging in size from 0.7 to greater than 3 megabasepairs. Relative staining intensities indicated that some bands contained multiple chromosomes. Major differences in the number, size, and intensity of bands allowed a clear differentiation of the karyotypes of isolates from each of the different individuals. This is in contrast to previous studies where the karyotype of different isolates have been strikingly homogeneous. Hybridization of Southern blots with surface antigen, beta-tubulin, and ribosomal RNA genes revealed that these gene families were distributed to different sized chromosomes amongst the different isolates. PFGE thus revealed major differences in the karyotypes of different G. lamblia isolates that were obtained over a short period of time from a relatively confined geographic area. In contrast, karyotypes of isolates established either by direct cultivation of duodenal trophozoites or by excystation of stool cysts from the same individuals were almost identical. Also, isolates from the same individuals obtained over a prolonged period of time revealed only minor differences in their karyotype, suggesting that recurrent infection can be caused by genetically similar organisms. We conclude that chronic giardiasis can result from recurrence of occult infection or reinfection from a common source.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam R. D., Aggarwal A., Lal A. A., de La Cruz V. F., McCutchan T., Nash T. E. Antigenic variation of a cysteine-rich protein in Giardia lamblia. J Exp Med. 1988 Jan 1;167(1):109–118. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.1.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam R. D., Nash T. E., Wellems T. E. The Giardia lamblia trophozoite contains sets of closely related chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4555–4567. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aggarwal A., Bhatia A., Naik S. R., Vinayak V. K. Variable virulence of isolates of Giardia lamblia in mice. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1983 Apr;77(2):163–167. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1983.11811692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baum K. F., Berens R. L., Jones R. H., Marr J. J. A new method for cloning Giardia lamblia, with a discussion of the statistical considerations of limiting dilution. J Parasitol. 1988 Apr;74(2):267–269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham A. K., Meyer E. A. Giardia excystation can be induced in vitro in acidic solutions. Nature. 1979 Jan 25;277(5694):301–302. doi: 10.1038/277301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boothroyd J. C., Wang A., Campbell D. A., Wang C. C. An unusually compact ribosomal DNA repeat in the protozoan Giardia lamblia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4065–4084. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell S. R., van Keulen H., Erlandsen S. L., Senturia J. B., Jarroll E. L. Giardia sp.: comparison of electrophoretic karyotypes. Exp Parasitol. 1990 Nov;71(4):470–482. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(90)90073-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillin F. D., Hagblom P., Harwood J., Aley S. B., Reiner D. S., McCaffery M., So M., Guiney D. G. Isolation and expression of the gene for a major surface protein of Giardia lamblia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4463–4467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordts B., Hemelhof W., Asselman C., Butzler J. P. In vitro susceptibilities of 25 Giardia lamblia isolates of human origin to six commonly used antiprotozoal agents. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1985 Sep;28(3):378–380. doi: 10.1128/aac.28.3.378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordts B., Hemelhof W., Van Tilborgh K., Retoré P., Cadranel S., Butzler J. P. Evaluation of a new method for routine in vitro cultivation of Giardia lamblia from human duodenal fluid. J Clin Microbiol. 1985 Nov;22(5):702–704. doi: 10.1128/jcm.22.5.702-704.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaac-Renton J. L., Byrne S. K., Prameya R. Isoelectric focusing of ten strains of Giardia duodenalis. J Parasitol. 1988 Dec;74(6):1054–1056. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz M., Korman S. H., Shapiro M., Har-Even U., Tamir I., Strauss N., Deckelbaum R. J. Asymptomatic giardiasis in children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 1989 Nov;8(11):773–779. doi: 10.1097/00006454-198911000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk-Mason K. E., Turner M. J., Chakraborty P. R. Cloning and sequence of beta tubulin cDNA from Giardia lamblia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2733–2733. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman S. H., Hais E., Spira D. T. Routine in vitro cultivation of Giardia lamblia by using the string test. J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Feb;28(2):368–369. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.2.368-369.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman S. H., Le Blancq S. M., Spira D. T., el On J., Reifen R. M., Deckelbaum R. J. Giardia lamblia: identification of different strains from man. Z Parasitenkd. 1986;72(2):173–180. doi: 10.1007/BF00931144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Blancq S. M., Kase R. S., Van der Ploeg L. H. Analysis of a Giardia lamblia rRNA encoding telomere with [TAGGG]n as the telomere repeat. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5790–5790. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Blancq S. M., Korman S. H., Van der Ploeg L. H. Frequent rearrangements of rRNA-encoding chromosomes in Giardia lamblia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4405–4412. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majewska A. C., Kasprzak W., De Jonckheere J. F., Kaczmarek E. Heterogeneity in the sensitivity of stocks and clones of Giardia to metronidazole and ornidazole. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1991 Jan-Feb;85(1):67–69. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(91)90161-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre P., Boreham P. F., Phillips R. E., Shepherd R. W. Chemotherapy in giardiasis: clinical responses and in vitro drug sensitivity of human isolates in axenic culture. J Pediatr. 1986 Jun;108(6):1005–1010. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80950-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloni B. P., Lymbery A. J., Thompson R. C. Characterization of Giardia isolates using a non-radiolabeled DNA probe, and correlation with the results of isoenzyme analysis. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1989 Jun;40(6):629–637. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1989.40.629. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meloni B. P., Lymbery A. J., Thompson R. C. Isoenzyme electrophoresis of 30 isolates of Giardia from humans and felines. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1988 Jan;38(1):65–73. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1988.38.65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. L., Wang A. L., Wang C. C. Identification of Giardia lamblia isolates susceptible and resistant to infection by the double-stranded RNA virus. Exp Parasitol. 1988 Jun;66(1):118–123. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(88)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Herrington D. A., Losonsky G. A., Levine M. M. Experimental human infections with Giardia lamblia. J Infect Dis. 1987 Dec;156(6):974–984. doi: 10.1093/infdis/156.6.974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., Keister D. B. Differences in excretory-secretory products and surface antigens among 19 isolates of Giardia. J Infect Dis. 1985 Dec;152(6):1166–1171. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.6.1166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash T. E., McCutchan T., Keister D., Dame J. B., Conrad J. D., Gillin F. D. Restriction-endonuclease analysis of DNA from 15 Giardia isolates obtained from humans and animals. J Infect Dis. 1985 Jul;152(1):64–73. doi: 10.1093/infdis/152.1.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield H. G., Bjorvat B. Ultrastructure of the cyst of Giardia lamblia. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1977 Jan;26(1):23–30. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1977.26.23. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. D., Gillin F. D., Spira W. M., Nash T. E. Chronic giardiasis: studies on drug sensitivity, toxin production, and host immune response. Gastroenterology. 1982 Oct;83(4):797–803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tannich E., Horstmann R. D., Knobloch J., Arnold H. H. Genomic DNA differences between pathogenic and nonpathogenic Entamoeba histolytica. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):5118–5122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.5118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upcroft J. A., Boreham P. F., Upcroft P. Geographic variation in Giardia karyotypes. Int J Parasitol. 1989 Aug;19(5):519–527. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(89)90082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upcroft P., Mitchell R., Boreham P. F. DNA fingerprinting of the intestinal parasite Giardia duodenalis with the M13 phage genome. Int J Parasitol. 1990 May;20(3):319–323. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(90)90146-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Cornelissen A. W., Michels P. A., Borst P. Chromosome rearrangements in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ploeg L. H., Smith C. L., Polvere R. I., Gottesdiener K. M. Improved separation of chromosome-sized DNA from Trypanosoma brucei, stock 427-60. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3217–3227. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Visvesvara G. S., Dickerson J. W., Healy G. R. Variable infectivity of human-derived Giardia lamblia cysts for Mongolian gerbils (Meriones unguiculatus). J Clin Microbiol. 1988 May;26(5):837–841. doi: 10.1128/jcm.26.5.837-841.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis P. M., Wallis H. M. Excystation and culturing of human and animal Giardia spp. by using gerbils and TYI-S-33 medium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Mar;51(3):647–651. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.3.647-651.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]