Figure 6.
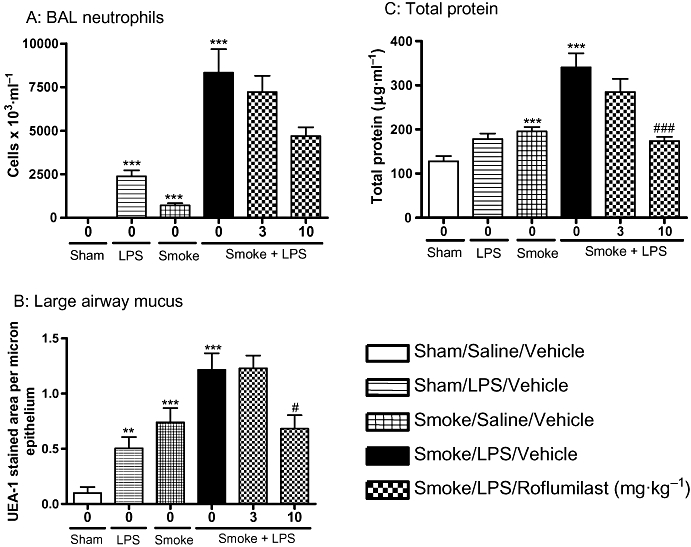
Roflumilast significantly reduced the inflammatory mediators induced by the combination of LPS and TS. Sprague-Dawley rats were exposed to tobacco smoke or air for 30 min twice a day for 2 days. On the morning of day 3 rats were exposed to saline of LPS (0.3 mg·mL−1) for 30 min followed by tobacco smoke or air 5 h later. One hour prior to each exposure animals were either dosed with vehicle or roflumilast (3 or 10 mg·kg−1). Twenty-four hours after LPS exposure (A) neutrophils (B) mucus and (C) total protein levels were assessed. Data represent the mean and SEM of n= 8 animals per group which was performed in one single experiment. (**P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 compared with air/saline controls; #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001 compared with LPS/smoke/vehicle control). BAL, broncho alveolar lavage; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; TS, tobacco smoke; UEA-1, Ulex europaeus agglutinin-1.
