Figure 4.
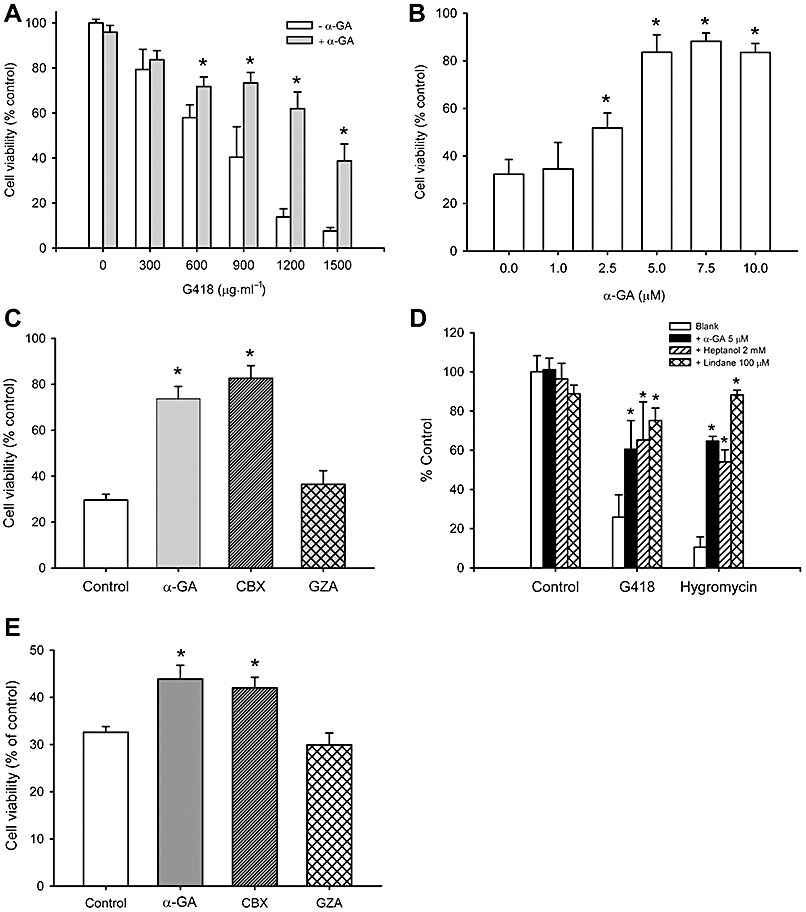
Gap junction inhibitors attenuate aminoglycosides-elicited cell injury in NRK-E52 cells. (A and B) Attenuation of drug-elicited cytotoxicity in NRK-E52 cells by α-GA. (A) NRK-E52 cells in confluent culture were exposed to various concentrations of G418 with or without α-GA (5 µM) for 48 h. (B) NRK-E52 cells were cultured with 1000 µg mL−1 G418 in the presence or absence of the indicated concentrations of α-GA for 48 h. (C) Effects of different analogues of α-GA on G418-elicited cytotoxicity. NRK-E52 cells were exposed to G418 (1000 µg mL−1) in the presence of 10 µM of α-GA, carbenoxolone (CBX), or glycyrrhizic acid (GZA) for 48 h. (D) Effect of different gap junction inhibitors on G418-elicited cytotoxicity. NRK-E52 cells were exposed to 1000 µg mL−1 G418 or 300 µg mL−1 hygromycin in the presence or absence of α-GA (5 µM), heptanol (2 mM) or lindane (100 µM) for 48 h. (E) Effects of different analogues of α-GA on gentamycin-elicited cytotoxicity. NRK-E52 cells were exposed to gentamycin (15 mg mL−1) in the presence of 10 µM of α-GA, CBX, or GZA for 48 h. Cell viability was evaluated by WST assay. Data are expressed as percentage of living cells, compared with the untreated control. *P < 0.01 versus untreated control.
