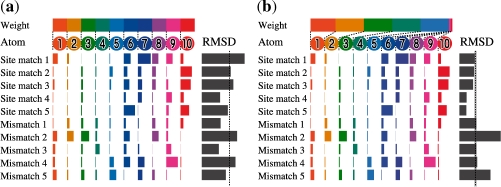
Fig. 1.
Example of metric learning. Computing RMSD is a typical means to search for site matches from numerous hits aligned with a query template. It involves taking the unweighted average of distances of each atom. This toy example shows a case in which each of the five site matches and five mismatches is aligned with a query template having 10 atoms. In this case, no threshold separates site matches from mismatches perfectly as long as the average of distances is unweighted, as shown in (a). Three mismatches and two site matches can be predicted incorrectly if the threshold depicted in (a) is used. Our metric learning algorithm finds a weight for each atom to generate a distance that separates site matches from mismatches. For this example, weighted RMSD supports a complete separation of site matches from mismatches, as shown in (b).