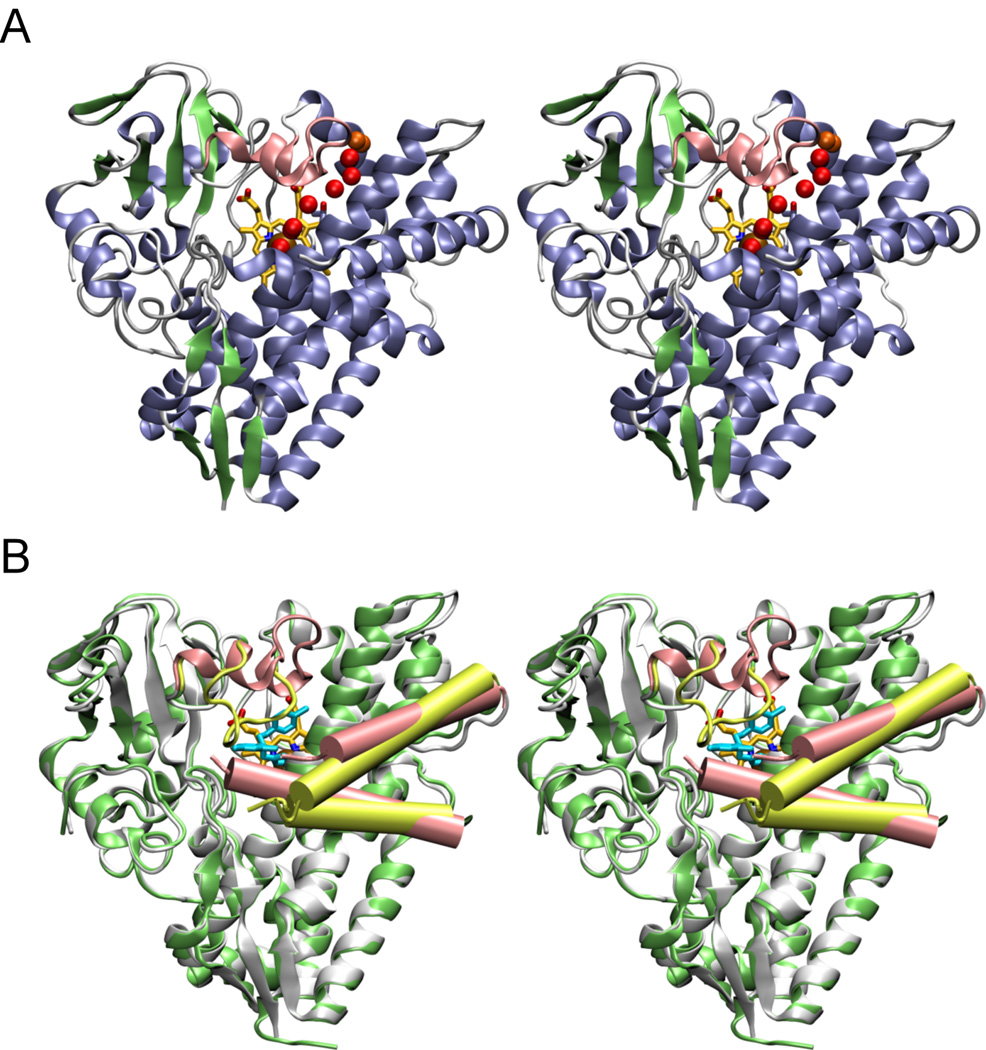
Fig. 3. Stereo views of ligand-free and econazole-bound CYP130.
A, the ligand-free CYP130 is in a ribbon representation colored according to the secondary structure elements: helices are in blue, β-sheets in green, and loops and turns in grey. The BC-loop region (highlighted in pink) is well-structured having two short helices αB' and αB". A hydrogen-bonding network of water molecules linking the stability of the distal water ligand to the I-helix N-terminus is marked by the red spheres. In orange are shown water molecules having contacts with the bulk solvent. Residue T239 in the N-terminal portion of the I-helix is shown in sticks. B, superimposition of the ligand-free (gray) and econazole-bound (lime green) forms. The BC-loop region containing residues 80–91 which relocates up to 18 Å to a position where they interact with the econazole is shown in pink in the ligand-free and in yellow-green in the econazole-bound forms. The F and G helices are shown as pink cylinders in the ligand-free and yellow-green cylinders in econazole bound forms. The G helix is on top. Econazole is in cyan and heme is in yellow. Images were generated using VMD software (51) unless specified otherwise.