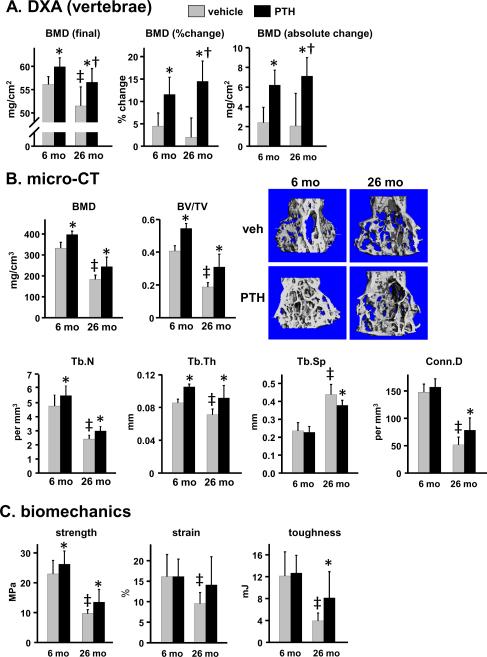
Figure 1.
Enhanced efficacy of intermittent PTH in vertebral trabecular bone of young vs. old old mice. Female C57BL/6 mice (N=9–12 per group) were given daily injections of vehicle or 100 ng/g PTH(1–34) for 28 days. (A) BMD was measured at the beginning and end of the experiment to allow calculation of % change and absolute magnitude of change caused by PTH. (B) Trabecular BMD, bone volume/tissue volume (BV/TV), trabecular number (Tb.N), trabecular thickness (Tb.Th), trabecular spacing (Tb.Sp) and connectivity density of the trabeculae (Conn.D) were determined in L4. Representative micro-CT images from each group of animals are shown. (C) Strength (load tolerated at the breaking point adjusted for bone size), strain (deformation tolerated before breaking), and toughness (energy required to break the bone) were measured in L5. Statistical analysis was done by 2-way ANOVA, except for BV/TV, Tb.Th, and Tb.N due to non-normal distribution of data. These parameters were analyzed by Kruskal-Wallis ANOVA on ranks. * p<0.05 vs. respective vehicle control; † p<0.05 vs. 6 month PTH response; ‡ p<0.05 vs. 6 month vehicle control.