Figure 8.
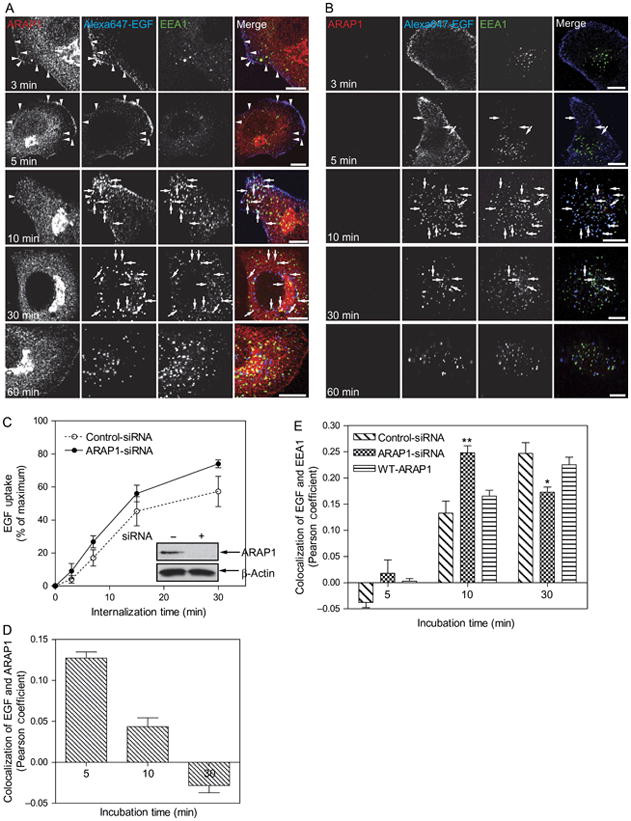
Effect of ARAP1 on EGF internalization. A) Time dependence of the relative localization of endogenous ARAP1, EGF and EEA1. HeLa Cells were treated with a nontargeting siRNA for 3 days prior to serum starvation and addition of 2 μg/mL of Alexa Fluor 647-labeled EGF. After the indicated length of time, cells were fixed and stained for endogenous ARAP1 and EEA1. EGF was visualized by Alexa Fluor 647 fluorescence. Arrowheads indicate colocalization of ARAP1 with Alexa Fluor 647-EGF, and arrows indicate colocalization of Alexa Fluor 647-EGF with EEA1. Scale bar, 10 μm. B) Effect of reduced ARAP1 expression on association with EEA1-positive compartment. HeLa cells treated with siRNA targeting ARAP1 were treated as described in (A). C) Time dependence of EGF internalization. Cells treated with nontargeting or ARAP1-siRNA were incubated with fluorescent EGF, and internalization was determined by FACS analysis as described in ‘Experimental Procedures’. Error bars are the SEM. D and E) Colocalization of EGF and ARAP1 (D) or EEA1 (E). Pearson coefficients were determined for 25 cells at each time-point. The error bars are the SEM. ** and * indicate significantly different from nontargeting-siRNA-treated cells, **p>0.001 and *p>0.01.
