Figure 1. Export of glycosylated and non-glycosylated variants of GspB736flag by accessory Sec deletion strains.
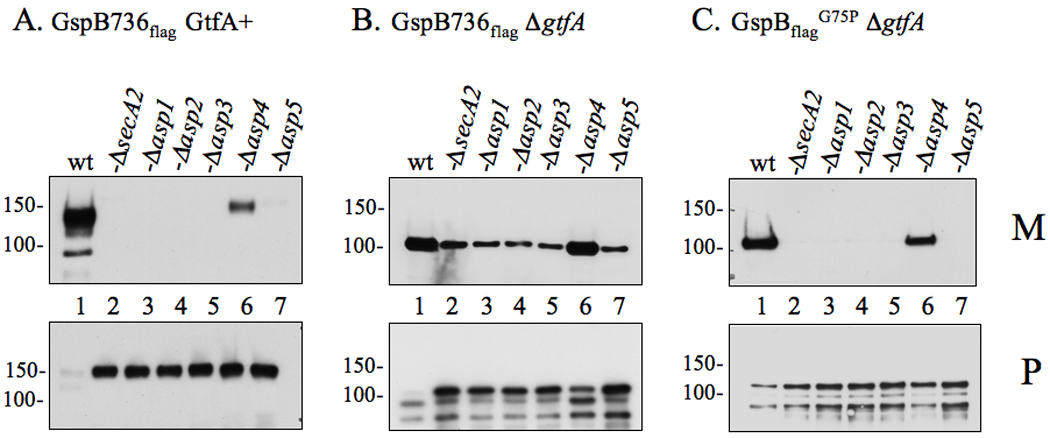
Proteins obtained from culture media (M) or lysed protoplasts (P) were separated by SDS-PAGE (3–8%) and probed with anti-FLAG antibody for GspB736flag detection. (A) Export of GspB736flag by the parent strain PS919 (Lane 1) or its accessory Sec deletion variants, PS920 (Lane 2), PS942 (Lane 3), PS944 (Lane 4), PS945 (Lane 5), PS925 (Lane 6), PS924 (Lane 7). (B) Export of nonglycosylated GspB736flag by PS1057 (Lane 1), or by accessory Sec/gtfA double deletion strains PS1063 (Lane 2), PS1060 (Lane 3), PS1061 (Lane 4), PS1062 (Lane 5), PS1059 (Lane 6), PS1058 (Lane 7). (C) Export of nonglycosylated GspB736flagG75P by PS1765 (Lane 1), or by accessory Sec/gtfA double deletion strains PS1208 (Lane 2), PS1768 (Lane 3), PS1769 (Lane 4), PS1770 (Lane 5), PS1771 (Lane 6), PS1772 (Lane 7). Glycosylated GspB is visible as a protein of approximately 140 or 150 kDa in the media or protoplasts respectively, while the non-glycosylated form is detected as a protein of approximately 100 or 110 kDa in size in the media or protoplasts respectively. Breakdown products of both forms of GspB are visible as smaller proteins accumulating within the protoplasts.
