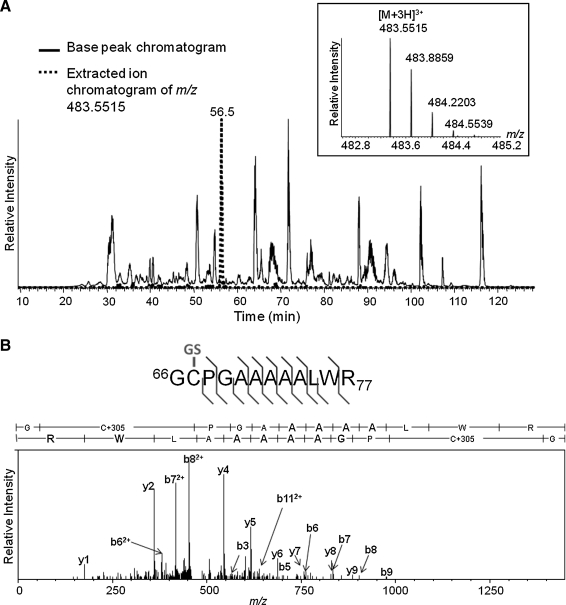
FIG. 4.
MS detection and sequencing of S-glutathiolated human SIRT1 peptide 66–77. Purified recombinant human SIRT1 was treated in vitro with GSNO, followed by NEM labeling of unreacted cysteines, and in-solution tryptic digestion. Peptides were subjected to nano-flow reversed-phase chromatography and MS/MS on an LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometer. (A) Base peak chromatogram (black trace) over the portion of the LC-MS run over which peptide elution occurs. Overlaid, the extracted ion chromatogram of the [M + 3H]3+ ion at m/z 483.5514 (red trace), which demonstrates that this species elutes distinctly during the 4 h total LC run at a retention time of ca. 56 min. Chromatographic peaks are labeled with the m/z value of their base peak. Inset (above) into the chromatogram is the mass spectrum of the [M + 3H]3+ ion species at m/z 483.5514 at its elution peak. (B) Fragment ion tandem mass spectrum resulting from the collisional dissociation of the [M + 3H]3+m/z 483.5514 precursor ion. Prominent fragment ions are marked with their assignments to b-type ions (right) and y-type ions (left) of the SIRT1 peptide 66GCPGAAAAALWR77 bearing a glutathione moiety on its cysteine. Above the spectrum, a summary of the fragment ion data, including less abundant fragment ions detected, is indicated on the peptide sequence by flags indicating b (right) and y (left) ions. The site of S-glutathiolation (indicated in green on the sequence) is identified unambiguously to the first three residues, therefore to Cys-67, by numerous prominent diagnostic b and y ions.