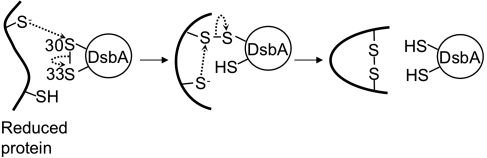
FIG. 3.
Disulfide-bond formation by DsbA. Substrate oxidation by DsbA likely proceeds through two steps. First, a deprotonated cysteine of a substrate attacks the sulfur atom of Cys30 of the oxidized DsbA, leading to the formation of a disulfide-linked complex between DsbA and the substrate. In the next step, one of the remaining cysteines of the substrate is deprotonated and attacks the sulfur atom of the substrate cysteine that is disulfide bonded with Cys30 of DsbA. This reaction results in the formation of a disulfide bond in the substrate and reduction of DsbA.