Abstract
The asymmetric unit of the title compound, [Cd2Cl2(NCS)2(C15H15NO2)2]n, contains the Schiff base 2-[(4-methylphenylimino)methyl]-6-methoxyphenol (HL) ligand, one thiocyanate and one chloride ligand coordinated to a cadmium centre. The cadmium centers are linked to each other via two thiocyanate and two chloride bridges alternately, resulting in centrosymmetric zigzag chains running parallel to the a axis. The CdII coordination environment contains two Cl atoms, one thiocyanate (SCN) S atom, one isothiocyanate (NCS) N atom and two O atoms from the HL ligand. The Schiff base ligand is in the trans conformation.
Related literature
For related literature regarding Schiff bases and their complexes, see: Mondal et al. (1999 ▶); Sen et al. (2006 ▶); Yi et al. (2004 ▶); Yu et al. (2007 ▶); Zhao et al. (2007 ▶); Zhou & Zhao (2007 ▶). For related structures, see: Ding et al. (2006 ▶); Suh et al. (2007 ▶).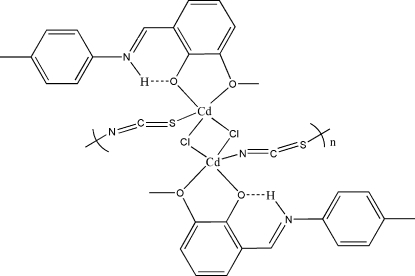
Experimental
Crystal data
[Cd2Cl2(NCS)2(C15H15NO2)2]
M r = 447.23
Triclinic,

a = 9.0485 (2) Å
b = 9.7321 (2) Å
c = 10.6676 (3) Å
α = 71.518 (2)°
β = 77.444 (2)°
γ = 80.732 (2)°
V = 865.32 (4) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.55 mm−1
T = 296 (2) K
0.27 × 0.11 × 0.08 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.82, T max = 0.882
13032 measured reflections
3940 independent reflections
3225 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.029
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.032
wR(F 2) = 0.081
S = 1.01
3940 reflections
208 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.54 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.52 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2006 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2006 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808038099/ez2146sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808038099/ez2146Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
salen-type Schiff bases are capable of forming complexes with different coordination modes, with certain metal ions. Some of these compounds have promising applications in catalysis, enzyme models and optical and magnetic materials (Sen et al., 2006). In addition, the unusual coordination modes of Schiff base ligands leads to unusual structures of the complexes. In previous articles (Zhou & Zhao, 2007; Yu et al., 2007; Zhao et al., 2007), we reported the synthesis and the ligating properties of the title Schiff base ligand, HL, derived from the condensation of o-vanillin and p-toluidine, to several transition and rare earth metals with different anions. In addition, many coordination polymers of one-, two-, and three-dimensional infinite frameworks involving cadmium(II) ions have been synthesized and studied due to their potential applications (Mondal et al., 1999). Coordination polymers of cadmium(II) have been exploited using anionic ligands, e.g., Cl-, Br-, I-, SCN-, N3-, SeCN-, etc., which are also an essential part of the coordination polyhedron, besides the organic ligand (Yi et al., 2004). Here we decribe the synthesis and crystal structure of a new cadmium(II) complex (Figure 1), [Cd(HL)(SCN)Cl]n, involving the Schiff base HL.
As shown in Fig. 1 and 2, each CdII atom is hexacoordinated by two Cl atoms, one thiocyanate S atom, one isothiocyanate N atom and two O atoms from the Schiff base ligand, HL. The HL ligand is in the trans conformation. The geometry around the CdII atom is a distorted octahedron. Neighbouring octahedral Cd centres are bridged by, alternately, the SCN and NCS ligands and two Cl ligands to form alternating eight-membered Cd—S—C—N—Cd—S—C—N– and four-membered Cd—Cl—Cd—Cl- rings. These chains run parallel to the a axis. The Cd—SSCN bond length is longer than the Cd—NNCS distance [2.7096 (11) versus 2.2484 (26) Å], which, together with the bond angles, are similar to related compounds in the literatures (Suh et al., 2007; Ding et al., 2006).
Experimental
First, the ligand was prepared by the direct solid-phase reaction of o-vanillin (10 mmol, 1.5251 g) and p-toluidine (10 mmol, 1.0700 g). The reactants were ground in an agate mortar. The color of the mixture changed from light yellow to orange. Then, for the preparation of the complex, a solution of CdCl2. 2.5H2O (1 mmol, 0.2931 g) and KSCN (0.1945 g, 2 mmol) in methanol (10 ml) was added to a methanol (30 ml) solution of the Schiff base ligand (2 mmol, 0.4826 g). Yellow crystals were obtained after 10 days.
Refinement
The H atoms bonded to C and N atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model [aromatic C—H=0.93 Å, aliphatic C—H = 0.97 (2) Å, N—H=0.86 Å, Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C,N)].
Figures
Fig. 1.
The coordination around the cadmium(II) center, showing the atom-labelling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A perspective view of the title compound along the b axis. H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| [Cd2Cl2(NCS)2(C15H15NO2)2] | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 447.23 | F000 = 444 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.717 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.0485 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 4749 reflections |
| b = 9.7321 (2) Å | θ = 2.1–27.4º |
| c = 10.6676 (3) Å | µ = 1.55 mm−1 |
| α = 71.518 (2)º | T = 296 (2) K |
| β = 77.444 (2)º | Block, red |
| γ = 80.732 (2)º | 0.27 × 0.11 × 0.08 mm |
| V = 865.32 (4) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII diffractometer | 3940 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3225 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.029 |
| T = 296(2) K | θmax = 27.4º |
| ω scans | θmin = 2.1º |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.82, Tmax = 0.882 | k = −12→12 |
| 13032 measured reflections | l = −13→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.032 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.081 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0453P)2 + 0.1806P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.01 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3940 reflections | Δρmax = 0.54 e Å−3 |
| 208 parameters | Δρmin = −0.52 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cd1 | 0.16960 (2) | 0.06238 (2) | 0.54427 (2) | 0.04022 (10) | |
| Cl1 | 0.05869 (9) | 0.10606 (10) | 0.33628 (8) | 0.0508 (2) | |
| O1 | −0.0129 (2) | 0.2707 (2) | 0.5970 (2) | 0.0479 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.2771 (3) | −0.0247 (3) | 0.9681 (2) | 0.0380 (5) | |
| H1D | 0.2767 | −0.0267 | 0.8882 | 0.046* | |
| C1 | 0.6806 (5) | −0.4746 (4) | 1.2474 (5) | 0.0786 (13) | |
| H1A | 0.6777 | −0.4648 | 1.3347 | 0.118* | |
| H1B | 0.7825 | −0.4685 | 1.1977 | 0.118* | |
| H1C | 0.6482 | −0.5672 | 1.2569 | 0.118* | |
| S1 | 0.64223 (10) | −0.27344 (10) | 0.58734 (12) | 0.0690 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.1735 (2) | 0.0798 (2) | 0.7460 (2) | 0.0448 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.5752 (4) | −0.3537 (4) | 1.1732 (4) | 0.0549 (9) | |
| N2 | 0.3597 (3) | −0.1180 (3) | 0.5586 (3) | 0.0555 (7) | |
| C3 | 0.4944 (4) | −0.2504 (4) | 1.2320 (4) | 0.0538 (9) | |
| H3A | 0.5066 | −0.2555 | 1.3178 | 0.065* | |
| C4 | 0.3960 (4) | −0.1396 (4) | 1.1679 (3) | 0.0472 (8) | |
| H4A | 0.3428 | −0.0712 | 1.2097 | 0.057* | |
| C5 | 0.3782 (3) | −0.1326 (3) | 1.0407 (3) | 0.0385 (7) | |
| C6 | 0.4605 (4) | −0.2321 (4) | 0.9780 (4) | 0.0541 (9) | |
| H6A | 0.4510 | −0.2254 | 0.8911 | 0.065* | |
| C7 | 0.5572 (4) | −0.3416 (4) | 1.0452 (4) | 0.0645 (10) | |
| H7A | 0.6116 | −0.4091 | 1.0029 | 0.077* | |
| C8 | 0.1852 (3) | 0.0767 (3) | 1.0080 (3) | 0.0405 (7) | |
| H8A | 0.1835 | 0.0824 | 1.0937 | 0.049* | |
| C9 | 0.0880 (3) | 0.1784 (3) | 0.9282 (3) | 0.0373 (6) | |
| C10 | −0.0067 (4) | 0.2857 (4) | 0.9810 (3) | 0.0543 (9) | |
| H10A | −0.0047 | 0.2876 | 1.0673 | 0.065* | |
| C11 | −0.0998 (4) | 0.3851 (4) | 0.9058 (4) | 0.0604 (10) | |
| H11A | −0.1604 | 0.4560 | 0.9404 | 0.073* | |
| C12 | −0.1062 (3) | 0.3829 (3) | 0.7766 (3) | 0.0464 (8) | |
| H12A | −0.1718 | 0.4514 | 0.7267 | 0.056* | |
| C13 | −0.0171 (3) | 0.2811 (3) | 0.7232 (3) | 0.0369 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.0858 (3) | 0.1752 (3) | 0.7971 (3) | 0.0334 (6) | |
| C15 | −0.1276 (4) | 0.3549 (4) | 0.5233 (3) | 0.0516 (8) | |
| H15A | −0.1801 | 0.4271 | 0.5654 | 0.077* | |
| H15B | −0.1987 | 0.2921 | 0.5221 | 0.077* | |
| H15C | −0.0812 | 0.4019 | 0.4330 | 0.077* | |
| C16 | 0.4777 (4) | −0.1803 (3) | 0.5696 (3) | 0.0441 (7) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cd1 | 0.03390 (14) | 0.05451 (16) | 0.03464 (15) | 0.00929 (10) | −0.01210 (9) | −0.01906 (11) |
| Cl1 | 0.0445 (4) | 0.0800 (6) | 0.0284 (4) | −0.0077 (4) | −0.0083 (3) | −0.0144 (4) |
| O1 | 0.0485 (12) | 0.0591 (13) | 0.0372 (12) | 0.0207 (10) | −0.0209 (10) | −0.0196 (10) |
| N1 | 0.0383 (13) | 0.0445 (13) | 0.0308 (14) | 0.0031 (11) | −0.0115 (10) | −0.0104 (11) |
| C1 | 0.056 (2) | 0.062 (2) | 0.100 (3) | −0.0001 (19) | −0.035 (2) | 0.012 (2) |
| S1 | 0.0392 (5) | 0.0516 (5) | 0.0980 (8) | 0.0070 (4) | −0.0190 (5) | 0.0023 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0492 (13) | 0.0502 (12) | 0.0392 (12) | 0.0204 (10) | −0.0211 (10) | −0.0226 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0390 (18) | 0.0470 (19) | 0.068 (3) | −0.0045 (15) | −0.0191 (17) | 0.0037 (17) |
| N2 | 0.0361 (15) | 0.0505 (16) | 0.076 (2) | 0.0055 (13) | −0.0112 (14) | −0.0172 (15) |
| C3 | 0.052 (2) | 0.063 (2) | 0.040 (2) | −0.0058 (17) | −0.0179 (16) | 0.0018 (16) |
| C4 | 0.0464 (18) | 0.0571 (19) | 0.0355 (18) | 0.0009 (15) | −0.0106 (14) | −0.0105 (15) |
| C5 | 0.0341 (15) | 0.0419 (16) | 0.0375 (17) | −0.0010 (12) | −0.0119 (13) | −0.0066 (13) |
| C6 | 0.052 (2) | 0.061 (2) | 0.051 (2) | 0.0156 (16) | −0.0234 (17) | −0.0204 (17) |
| C7 | 0.057 (2) | 0.062 (2) | 0.079 (3) | 0.0174 (18) | −0.025 (2) | −0.030 (2) |
| C8 | 0.0395 (17) | 0.0526 (18) | 0.0284 (16) | −0.0012 (14) | −0.0054 (13) | −0.0125 (13) |
| C9 | 0.0336 (15) | 0.0459 (16) | 0.0314 (16) | 0.0038 (13) | −0.0064 (12) | −0.0132 (13) |
| C10 | 0.056 (2) | 0.069 (2) | 0.0392 (19) | 0.0146 (17) | −0.0108 (16) | −0.0249 (17) |
| C11 | 0.058 (2) | 0.069 (2) | 0.058 (2) | 0.0254 (18) | −0.0117 (18) | −0.0367 (19) |
| C12 | 0.0386 (17) | 0.0500 (18) | 0.0453 (19) | 0.0127 (14) | −0.0117 (14) | −0.0123 (15) |
| C13 | 0.0337 (15) | 0.0425 (16) | 0.0338 (16) | 0.0011 (12) | −0.0088 (12) | −0.0106 (13) |
| C14 | 0.0290 (14) | 0.0377 (15) | 0.0323 (16) | 0.0005 (11) | −0.0056 (11) | −0.0104 (12) |
| C15 | 0.0463 (19) | 0.062 (2) | 0.044 (2) | 0.0107 (16) | −0.0222 (15) | −0.0110 (16) |
| C16 | 0.0392 (17) | 0.0434 (17) | 0.048 (2) | −0.0021 (14) | −0.0039 (14) | −0.0144 (14) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cd1—O2 | 2.2191 (19) | C3—C4 | 1.383 (4) |
| Cd1—N2 | 2.244 (3) | C3—H3A | 0.9300 |
| Cd1—Cl1 | 2.5187 (8) | C4—C5 | 1.381 (4) |
| Cd1—O1 | 2.529 (2) | C4—H4A | 0.9300 |
| Cd1—Cl1i | 2.6833 (9) | C5—C6 | 1.379 (4) |
| Cd1—S1ii | 2.7107 (10) | C6—C7 | 1.380 (5) |
| Cl1—Cd1i | 2.6833 (9) | C6—H6A | 0.9300 |
| O1—C13 | 1.373 (3) | C7—H7A | 0.9300 |
| O1—C15 | 1.428 (4) | C8—C9 | 1.410 (4) |
| N1—C8 | 1.303 (4) | C8—H8A | 0.9300 |
| N1—C5 | 1.421 (4) | C9—C14 | 1.413 (4) |
| N1—H1D | 0.8600 | C9—C10 | 1.420 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.515 (5) | C10—C11 | 1.352 (5) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9600 | C10—H10A | 0.9300 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9600 | C11—C12 | 1.400 (5) |
| C1—H1C | 0.9600 | C11—H11A | 0.9300 |
| S1—C16 | 1.629 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.362 (4) |
| S1—Cd1ii | 2.7107 (10) | C12—H12A | 0.9300 |
| O2—C14 | 1.299 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.430 (4) |
| C2—C7 | 1.376 (5) | C15—H15A | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.379 (5) | C15—H15B | 0.9600 |
| N2—C16 | 1.150 (4) | C15—H15C | 0.9600 |
| O2—Cd1—N2 | 92.93 (9) | C3—C4—H4A | 120.7 |
| O2—Cd1—Cl1 | 155.30 (6) | C6—C5—C4 | 120.3 (3) |
| N2—Cd1—Cl1 | 110.91 (8) | C6—C5—N1 | 117.0 (3) |
| O2—Cd1—O1 | 67.95 (7) | C4—C5—N1 | 122.7 (3) |
| N2—Cd1—O1 | 160.37 (10) | C5—C6—C7 | 119.4 (3) |
| Cl1—Cd1—O1 | 88.62 (5) | C5—C6—H6A | 120.3 |
| O2—Cd1—Cl1i | 86.93 (6) | C7—C6—H6A | 120.3 |
| N2—Cd1—Cl1i | 96.98 (7) | C2—C7—C6 | 121.8 (3) |
| Cl1—Cd1—Cl1i | 83.92 (3) | C2—C7—H7A | 119.1 |
| O1—Cd1—Cl1i | 86.77 (6) | C6—C7—H7A | 119.1 |
| O2—Cd1—S1ii | 94.23 (6) | N1—C8—C9 | 123.5 (3) |
| N2—Cd1—S1ii | 93.69 (8) | N1—C8—H8A | 118.3 |
| Cl1—Cd1—S1ii | 90.71 (3) | C9—C8—H8A | 118.3 |
| O1—Cd1—S1ii | 83.73 (6) | C8—C9—C14 | 120.8 (2) |
| Cl1i—Cd1—S1ii | 169.20 (3) | C8—C9—C10 | 118.9 (3) |
| Cd1—Cl1—Cd1i | 96.08 (3) | C14—C9—C10 | 120.3 (3) |
| C13—O1—C15 | 118.3 (2) | C11—C10—C9 | 119.9 (3) |
| C13—O1—Cd1 | 113.42 (16) | C11—C10—H10A | 120.0 |
| C15—O1—Cd1 | 126.96 (18) | C9—C10—H10A | 120.0 |
| C8—N1—C5 | 127.9 (3) | C10—C11—C12 | 121.0 (3) |
| C8—N1—H1D | 116.1 | C10—C11—H11A | 119.5 |
| C5—N1—H1D | 116.1 | C12—C11—H11A | 119.5 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.5 | C13—C12—C11 | 120.5 (3) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C13—C12—H12A | 119.7 |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C11—C12—H12A | 119.7 |
| C2—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C12—C13—O1 | 125.2 (3) |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C12—C13—C14 | 121.0 (3) |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | O1—C13—C14 | 113.9 (2) |
| C16—S1—Cd1ii | 100.35 (12) | O2—C14—C9 | 121.3 (3) |
| C14—O2—Cd1 | 123.29 (18) | O2—C14—C13 | 121.4 (3) |
| C7—C2—C3 | 117.5 (3) | C9—C14—C13 | 117.3 (2) |
| C7—C2—C1 | 121.8 (4) | O1—C15—H15A | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.7 (4) | O1—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C16—N2—Cd1 | 160.6 (3) | H15A—C15—H15B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 122.3 (3) | O1—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 118.8 | H15A—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 118.8 | H15B—C15—H15C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.6 (3) | N2—C16—S1 | 178.1 (3) |
| C5—C4—H4A | 120.7 | ||
| O2—Cd1—Cl1—Cd1i | −68.87 (15) | C8—N1—C5—C6 | 177.7 (3) |
| N2—Cd1—Cl1—Cd1i | 95.17 (8) | C8—N1—C5—C4 | −2.6 (5) |
| O1—Cd1—Cl1—Cd1i | −86.90 (6) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | 2.1 (5) |
| Cl1i—Cd1—Cl1—Cd1i | 0.0 | N1—C5—C6—C7 | −178.2 (3) |
| S1ii—Cd1—Cl1—Cd1i | −170.61 (3) | C3—C2—C7—C6 | −0.9 (6) |
| O2—Cd1—O1—C13 | −2.23 (18) | C1—C2—C7—C6 | 179.6 (3) |
| N2—Cd1—O1—C13 | −16.0 (4) | C5—C6—C7—C2 | −0.7 (6) |
| Cl1—Cd1—O1—C13 | 169.75 (19) | C5—N1—C8—C9 | −179.5 (3) |
| Cl1i—Cd1—O1—C13 | 85.76 (19) | N1—C8—C9—C14 | −0.1 (5) |
| S1ii—Cd1—O1—C13 | −99.38 (19) | N1—C8—C9—C10 | −179.3 (3) |
| O2—Cd1—O1—C15 | −169.0 (3) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | 179.4 (3) |
| N2—Cd1—O1—C15 | 177.2 (3) | C14—C9—C10—C11 | 0.2 (5) |
| Cl1—Cd1—O1—C15 | 3.0 (2) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.0 (6) |
| Cl1i—Cd1—O1—C15 | −81.0 (2) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.8 (6) |
| S1ii—Cd1—O1—C15 | 93.8 (2) | C11—C12—C13—O1 | −178.9 (3) |
| N2—Cd1—O2—C14 | 177.8 (2) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.6 (5) |
| Cl1—Cd1—O2—C14 | −17.1 (3) | C15—O1—C13—C12 | −11.6 (5) |
| O1—Cd1—O2—C14 | 2.4 (2) | Cd1—O1—C13—C12 | −179.6 (3) |
| Cl1i—Cd1—O2—C14 | −85.3 (2) | C15—O1—C13—C14 | 169.9 (3) |
| S1ii—Cd1—O2—C14 | 83.9 (2) | Cd1—O1—C13—C14 | 1.9 (3) |
| O2—Cd1—N2—C16 | −59.5 (9) | Cd1—O2—C14—C9 | 177.4 (2) |
| Cl1—Cd1—N2—C16 | 127.1 (9) | Cd1—O2—C14—C13 | −2.4 (4) |
| O1—Cd1—N2—C16 | −46.8 (10) | C8—C9—C14—O2 | −0.5 (4) |
| Cl1i—Cd1—N2—C16 | −146.8 (9) | C10—C9—C14—O2 | 178.7 (3) |
| S1ii—Cd1—N2—C16 | 34.9 (9) | C8—C9—C14—C13 | 179.3 (3) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | 1.3 (5) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | −1.4 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.2 (3) | C12—C13—C14—O2 | −178.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.1 (5) | O1—C13—C14—O2 | 0.0 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −1.8 (5) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | 1.7 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 178.5 (3) | O1—C13—C14—C9 | −179.8 (3) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: EZ2146).
References
- Bruker (2006). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Ding, B., Yi, L., Wang, Y., Cheng, P., Liao, D. Z., Yan, S. P., Jiang, Z. H., Song, H. B. & Wang, H. G. (2006). Dalton Trans. pp. 665–675. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mondal, A., Mostafa, G., Ghosh, A., Laskar, I. R. & Chaudhuri, N. R. (1999). J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. pp. 9–10.
- Sen, S., Talukder, P., Dey, S. K., Mitra, S., Rosair, G., Hughes, D. L., Yap, G. P. A., Pilet, G., Gramlich, V. & Matsushita, T. (2006). Dalton Trans. pp. 1758–1767. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Suh, S. W., Kim, C.-H. & Kim, I. H. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, m2177.
- Yi, L., Ding, B., Zhao, B., Cheng, P., Liao, D. Z., Yan, S. P. & Jiang, Z. H. (2004). Inorg. Chem.43, 33–43. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y. Y., Zhao, G. L. & Wen, Y. H. (2007). Chin. J. Struct. Chem.26, 1395–1402.
- Zhao, G.-L., Shi, X. & Ng, S. W. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, m267–m268.
- Zhou, Y.-H. & Zhao, G.-L. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, m43–m44.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808038099/ez2146sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808038099/ez2146Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




