Abstract
The title compound (systematic name: 4,7-methano-2,2′-spirobi[1,3-benzodioxole]), C14H14O4, is an asymmetric spiro ester of orthocarbonic acid and two diols, viz. the aromatic benzene-1,2-diol and the aliphatic vicinal norbornane-exo-cis-2,3-diol. The orthocarbonate molecule is close to having non-crystallographic C s symmetry. The five-membered ring stemming from the aliphatic diol has an envelope conformation. C—O bonds including the spiro-C atom span an approximately 0.07 Å range, but are within 0.02 Å of the respective distances in a density functional theory calculation, i.e. the distance difference is not caused by packing forces. Accordingly, the crystal packing is characterized by weak C—H⋯O and C—H⋯π interactions.
Related literature
For the synthesis of the title compound, see: Komatsu et al. (1992 ▶). For related compounds, see: Betz & Klüfers (2007a
▶,b
▶,c
▶); Betz et al. (2007 ▶). Density functional theory calculations were performed by Betz & Klüfers (2008 ▶).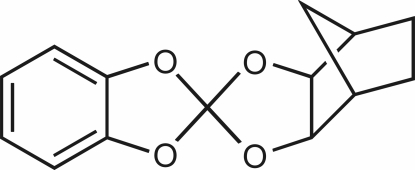
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H14O4
M r = 246.25
Monoclinic,

a = 7.9125 (3) Å
b = 9.5545 (5) Å
c = 15.2813 (6) Å
β = 101.490 (3)°
V = 1132.11 (9) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 200 (2) K
0.30 × 0.25 × 0.16 mm
Data collection
Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
8399 measured reflections
2582 independent reflections
1716 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.054
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.044
wR(F 2) = 0.119
S = 1.05
2582 reflections
164 parameters
Only H-atom displacement parameters refined
Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3
Data collection: COLLECT (Nonius, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SCALEPACK (Otwinowski & Minor 1997 ▶); data reduction: DENZO (Otwinowski & Minor 1997 ▶) and SCALEPACK; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: PLATON (Spek, 2003 ▶; 2006 version).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807063660/lx2027sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807063660/lx2027Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| O1—C1 | 1.367 (2) |
| O2—C1 | 1.370 (2) |
| O3—C1 | 1.412 (2) |
| O4—C1 | 1.435 (2) |
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
Cg is the centroid of the C9–C14 phenylene ring.
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C3—H3⋯O4i | 1.00 | 2.71 | 3.623 (2) | 151 |
| C7—H7A⋯O4i | 0.99 | 2.76 | 3.663 (2) | 151 |
| C14—H14⋯O2ii | 0.95 | 2.61 | 3.501 (2) | 156 |
| C14—H14⋯O4ii | 0.95 | 2.88 | 3.514 (2) | 125 |
| C2—H2⋯Cgiii | 1.00 | 2.86 | 3.563 (2) | 128 |
| C5—H5⋯Cgiv | 1.00 | 2.66 | 3.568 (2) | 152 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Moritz Reichvilser for professional support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The title compound was prepared in order to compare its NMR-spectroscopic data with those of related silicon compounds.
In the molecule, a central carbon atom is chelated by a phenylene-1,2-dioxy and a norbornylene-exo-cis-2,3-dioxy moiety. The C—O bond lengths differ markedly (1.37 to 1.44 Å). About the same bond-length values were computed for the isolated molecule on the B3LYP/6–31+G(d,p) level of theory thus ruling out packing forces as the origin of the bond-length differences. The five-membered chelate ring stemming from the aliphatic diol adopts an envelope conformation on the spiro center C1 (puckering parameters: Q2 = 0.1274 (16) Å, φ2 = 42.6 (7)° for the O1—C1—O2—C4—C3 ring).
Accordingly, the crystal packing is characterized by weak C—H···X interactions whose H···X distances are close to the sum of the van-der-Waals radii (vdWr). In terms of the vdWr criterion, the shortest tabulated hydrogen-bond, the C14—H14···O2 interaction, is 0.11 \&A shorter than the radii sum. The weak interactions in (I) are thus less significant than those in the related 1-(ylomethyl)cyclopentyl 1',2'-phenylene orthocarbonate, where C—H···O bonds are observed at the radii sum minus 0.35 Å (Betz & Klüfers, 2007c). Fig. 2 shows this interaction as well as the shortest C—H···π bond which has one of the norbornane-bridgehead C—H functions as the donor. The other bridgehead methylidyne function acts as a donor in a still weaker bond. Moreover, another weak C—H···O bond may be recognized with a diol-CH function as the donor (see the hydrogen bond table).
Experimental
The title compound was prepared based on a published procedure (Komatsu et al., 1992) upon reaction of norbornane-exo-cis-2,3-diol with 2,2-dichlorobenzo[1.3]dioxol in dichloromethane in the presence of pyridine. Crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained after recrystallization from boiling ethyl acetate.
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model, with C—H distances of 0.95, 0.99 and 1.00 Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) for all H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, showing displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing viewed along [0 1 0]. Green arrows: the strongest C—H···O interaction in terms of the H···O distance (C14—H14···O2). Green dotted lines: the strongest C—H···π interaction (C5—H5—Cg, Cg is the centroid of the phenylene residue).
Crystal data
| C14H14O4 | F000 = 520 |
| Mr = 246.25 | Dx = 1.445 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 14429 reflections |
| a = 7.9125 (3) Å | θ = 2.7–27.5º |
| b = 9.5545 (5) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| c = 15.2813 (6) Å | T = 200 (2) K |
| β = 101.490 (3)º | Block, colourless |
| V = 1132.11 (9) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.25 × 0.16 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Nonius KappaCCD diffractometer | 1716 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: rotating anode | Rint = 0.054 |
| Monochromator: MONTEL, graded multilayered X-ray optics | θmax = 27.5º |
| T = 200(2) K | θmin = 3.2º |
| CCD; rotation images; thick slices scans | h = −9→10 |
| Absorption correction: none | k = −12→11 |
| 8399 measured reflections | l = −19→19 |
| 2582 independent reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | Only H-atom displacement parameters refined |
| wR(F2) = 0.119 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0569P)2 + 0.1349P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.05 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 2582 reflections | Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3 |
| 164 parameters | Δρmin = −0.19 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.39573 (14) | 0.24072 (14) | 0.47478 (7) | 0.0460 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.51722 (14) | 0.20489 (14) | 0.35623 (7) | 0.0463 (3) | |
| O3 | 0.27667 (13) | 0.34038 (12) | 0.34119 (7) | 0.0408 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.25466 (14) | 0.10405 (11) | 0.35921 (8) | 0.0441 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.3646 (2) | 0.22289 (18) | 0.38424 (11) | 0.0384 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.67414 (19) | 0.32183 (17) | 0.56079 (10) | 0.0333 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.6161 | 0.3766 | 0.6022 | 0.0490 (13)* | |
| C3 | 0.56971 (19) | 0.20081 (17) | 0.51341 (10) | 0.0342 (4) | |
| H3 | 0.5742 | 0.1165 | 0.5526 | 0.0490 (13)* | |
| C4 | 0.65286 (19) | 0.17354 (18) | 0.43193 (10) | 0.0368 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.6964 | 0.0755 | 0.4305 | 0.0490 (13)* | |
| C5 | 0.7973 (2) | 0.28116 (18) | 0.44257 (11) | 0.0378 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.8407 | 0.3025 | 0.3869 | 0.0490 (13)* | |
| C6 | 0.9350 (2) | 0.2320 (2) | 0.52188 (12) | 0.0458 (5) | |
| H6A | 1.0433 | 0.2857 | 0.5259 | 0.0490 (13)* | |
| H6B | 0.9600 | 0.1310 | 0.5171 | 0.0490 (13)* | |
| C7 | 0.8509 (2) | 0.26146 (19) | 0.60315 (11) | 0.0439 (4) | |
| H7A | 0.8387 | 0.1743 | 0.6364 | 0.0490 (13)* | |
| H7B | 0.9196 | 0.3298 | 0.6443 | 0.0490 (13)* | |
| C8 | 0.7165 (2) | 0.40464 (17) | 0.48246 (10) | 0.0384 (4) | |
| H8A | 0.6123 | 0.4412 | 0.4420 | 0.0490 (13)* | |
| H8B | 0.7995 | 0.4814 | 0.5018 | 0.0490 (13)* | |
| C9 | 0.12113 (18) | 0.29423 (16) | 0.29208 (9) | 0.0307 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.10837 (18) | 0.15188 (16) | 0.30274 (9) | 0.0307 (4) | |
| C11 | −0.03269 (19) | 0.07732 (17) | 0.26098 (10) | 0.0365 (4) | |
| H11 | −0.0406 | −0.0211 | 0.2681 | 0.0490 (13)* | |
| C12 | −0.16353 (19) | 0.15365 (18) | 0.20764 (10) | 0.0367 (4) | |
| H12 | −0.2643 | 0.1064 | 0.1778 | 0.0490 (13)* | |
| C13 | −0.1506 (2) | 0.29664 (18) | 0.19700 (10) | 0.0375 (4) | |
| H13 | −0.2426 | 0.3454 | 0.1600 | 0.0490 (13)* | |
| C14 | −0.0054 (2) | 0.37112 (17) | 0.23937 (10) | 0.0350 (4) | |
| H14 | 0.0049 | 0.4693 | 0.2320 | 0.0490 (13)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0254 (6) | 0.0743 (9) | 0.0367 (7) | 0.0025 (5) | 0.0027 (5) | −0.0082 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0296 (6) | 0.0719 (9) | 0.0354 (6) | 0.0024 (6) | 0.0016 (5) | −0.0142 (6) |
| O3 | 0.0331 (6) | 0.0367 (7) | 0.0486 (7) | −0.0050 (5) | −0.0018 (5) | −0.0036 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0333 (6) | 0.0351 (7) | 0.0556 (7) | 0.0031 (5) | −0.0107 (5) | 0.0028 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0293 (9) | 0.0449 (10) | 0.0388 (9) | 0.0000 (7) | 0.0014 (7) | −0.0057 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0337 (8) | 0.0357 (9) | 0.0301 (8) | 0.0013 (7) | 0.0053 (6) | −0.0024 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0283 (8) | 0.0362 (9) | 0.0369 (8) | −0.0013 (6) | 0.0034 (6) | 0.0023 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0305 (8) | 0.0389 (9) | 0.0389 (9) | 0.0032 (7) | 0.0016 (6) | −0.0092 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0297 (8) | 0.0489 (10) | 0.0358 (9) | −0.0022 (7) | 0.0089 (6) | −0.0042 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0283 (9) | 0.0509 (11) | 0.0552 (11) | 0.0031 (7) | 0.0015 (7) | −0.0084 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0365 (9) | 0.0506 (11) | 0.0401 (10) | −0.0041 (8) | −0.0031 (7) | 0.0004 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0419 (9) | 0.0320 (9) | 0.0419 (9) | −0.0018 (7) | 0.0096 (7) | 0.0023 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0267 (8) | 0.0362 (9) | 0.0293 (8) | −0.0017 (6) | 0.0059 (6) | −0.0036 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0261 (8) | 0.0336 (9) | 0.0315 (8) | 0.0037 (6) | 0.0033 (6) | 0.0010 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0320 (8) | 0.0335 (9) | 0.0432 (9) | −0.0027 (7) | 0.0057 (6) | −0.0007 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0261 (8) | 0.0478 (11) | 0.0351 (8) | −0.0012 (7) | 0.0030 (6) | −0.0050 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0318 (8) | 0.0468 (11) | 0.0326 (8) | 0.0083 (7) | 0.0035 (6) | 0.0031 (7) |
| C14 | 0.0388 (9) | 0.0328 (9) | 0.0346 (8) | 0.0043 (7) | 0.0102 (7) | 0.0046 (7) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C1 | 1.367 (2) | C5—H5 | 1.0000 |
| O1—C3 | 1.438 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.547 (3) |
| O2—C1 | 1.370 (2) | C6—H6A | 0.9900 |
| O2—C4 | 1.444 (2) | C6—H6B | 0.9900 |
| O3—C9 | 1.380 (2) | C7—H7A | 0.9900 |
| O3—C1 | 1.412 (2) | C7—H7B | 0.9900 |
| O4—C10 | 1.377 (2) | C8—H8A | 0.9900 |
| O4—C1 | 1.435 (2) | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| C2—C3 | 1.518 (2) | C9—C14 | 1.367 (2) |
| C2—C8 | 1.527 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.376 (2) |
| C2—C7 | 1.532 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.370 (2) |
| C2—H2 | 1.0000 | C11—C12 | 1.390 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.542 (2) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C3—H3 | 1.0000 | C12—C13 | 1.382 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.522 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4 | 1.0000 | C13—C14 | 1.396 (2) |
| C5—C8 | 1.526 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.533 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C1—O1—C3 | 110.32 (12) | C5—C6—H6A | 111.1 |
| C1—O2—C4 | 109.66 (12) | C7—C6—H6A | 111.1 |
| C9—O3—C1 | 107.62 (12) | C5—C6—H6B | 111.1 |
| C10—O4—C1 | 107.09 (12) | C7—C6—H6B | 111.1 |
| O1—C1—O2 | 109.88 (12) | H6A—C6—H6B | 109.1 |
| O1—C1—O3 | 110.18 (13) | C2—C7—C6 | 103.41 (13) |
| O2—C1—O3 | 109.73 (14) | C2—C7—H7A | 111.1 |
| O1—C1—O4 | 110.22 (14) | C6—C7—H7A | 111.1 |
| O2—C1—O4 | 110.04 (13) | C2—C7—H7B | 111.1 |
| O3—C1—O4 | 106.75 (11) | C6—C7—H7B | 111.1 |
| C3—C2—C8 | 101.79 (12) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.0 |
| C3—C2—C7 | 106.20 (13) | C5—C8—C2 | 95.02 (13) |
| C8—C2—C7 | 101.65 (13) | C5—C8—H8A | 112.7 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 115.2 | C2—C8—H8A | 112.7 |
| C8—C2—H2 | 115.2 | C5—C8—H8B | 112.7 |
| C7—C2—H2 | 115.2 | C2—C8—H8B | 112.7 |
| O1—C3—C2 | 112.31 (13) | H8A—C8—H8B | 110.2 |
| O1—C3—C4 | 103.94 (12) | C14—C9—C10 | 122.58 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 103.56 (12) | C14—C9—O3 | 128.15 (15) |
| O1—C3—H3 | 112.1 | C10—C9—O3 | 109.27 (13) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 112.1 | C11—C10—C9 | 122.08 (14) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 112.1 | C11—C10—O4 | 128.66 (14) |
| O2—C4—C5 | 111.59 (13) | C9—C10—O4 | 109.27 (12) |
| O2—C4—C3 | 104.08 (12) | C10—C11—C12 | 116.29 (15) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 103.40 (12) | C10—C11—H11 | 121.9 |
| O2—C4—H4 | 112.4 | C12—C11—H11 | 121.9 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 112.4 | C13—C12—C11 | 121.58 (14) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 112.4 | C13—C12—H12 | 119.2 |
| C4—C5—C8 | 101.52 (13) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.2 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 106.13 (14) | C12—C13—C14 | 121.51 (14) |
| C8—C5—C6 | 102.10 (13) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.2 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 115.1 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.2 |
| C8—C5—H5 | 115.1 | C9—C14—C13 | 115.96 (15) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 115.1 | C9—C14—H14 | 122.0 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 103.11 (13) | C13—C14—H14 | 122.0 |
| C3—O1—C1—O2 | −14.26 (19) | O2—C4—C5—C6 | −177.46 (13) |
| C3—O1—C1—O3 | −135.27 (13) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | 71.25 (15) |
| C3—O1—C1—O4 | 107.18 (14) | C4—C5—C6—C7 | −72.05 (16) |
| C4—O2—C1—O1 | 15.22 (19) | C8—C5—C6—C7 | 33.89 (17) |
| C4—O2—C1—O3 | 136.51 (13) | C3—C2—C7—C6 | 70.90 (16) |
| C4—O2—C1—O4 | −106.32 (14) | C8—C2—C7—C6 | −35.19 (16) |
| C9—O3—C1—O1 | −119.98 (13) | C5—C6—C7—C2 | 0.83 (17) |
| C9—O3—C1—O2 | 118.91 (13) | C4—C5—C8—C2 | 54.90 (14) |
| C9—O3—C1—O4 | −0.31 (16) | C6—C5—C8—C2 | −54.59 (14) |
| C10—O4—C1—O1 | 120.17 (13) | C3—C2—C8—C5 | −54.54 (14) |
| C10—O4—C1—O2 | −118.49 (14) | C7—C2—C8—C5 | 54.98 (14) |
| C10—O4—C1—O3 | 0.52 (17) | C1—O3—C9—C14 | −179.57 (15) |
| C1—O1—C3—C2 | 118.72 (15) | C1—O3—C9—C10 | −0.02 (16) |
| C1—O1—C3—C4 | 7.43 (17) | C14—C9—C10—C11 | 0.0 (2) |
| C8—C2—C3—O1 | −77.54 (15) | O3—C9—C10—C11 | −179.53 (14) |
| C7—C2—C3—O1 | 176.46 (13) | C14—C9—C10—O4 | 179.94 (14) |
| C8—C2—C3—C4 | 33.98 (15) | O3—C9—C10—O4 | 0.36 (17) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −72.02 (14) | C1—O4—C10—C11 | 179.34 (16) |
| C1—O2—C4—C5 | −120.76 (14) | C1—O4—C10—C9 | −0.54 (17) |
| C1—O2—C4—C3 | −9.90 (17) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.6 (2) |
| O1—C3—C4—O2 | 1.48 (16) | O4—C10—C11—C12 | 179.57 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—O2 | −116.04 (13) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.5 (2) |
| O1—C3—C4—C5 | 118.21 (13) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.0 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.68 (15) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | 0.5 (2) |
| O2—C4—C5—C8 | 76.19 (15) | O3—C9—C14—C13 | 179.99 (14) |
| C3—C4—C5—C8 | −35.11 (15) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | −0.5 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C3—H3···O4i | 1.00 | 2.71 | 3.623 (2) | 151 |
| C7—H7A···O4i | 0.99 | 2.76 | 3.663 (2) | 151 |
| C14—H14···O2ii | 0.95 | 2.61 | 3.501 (2) | 156 |
| C14—H14···O4ii | 0.95 | 2.88 | 3.514 (2) | 125 |
| C2—H2···Cgiii | 1.00 | 2.86 | 3.563 (2) | 128 |
| C5—H5···Cgiv | 1.00 | 2.66 | 3.568 (2) | 152 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x+1/2, y+1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) x−1/2, −y−1/2, z−1/2; (iv) x+1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: LX2027).
References
- Betz, R., Jahn, N. & Klüfers, P. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o4152.
- Betz, R. & Klüfers, P. (2007a). Acta Cryst. E63, o3933.
- Betz, R. & Klüfers, P. (2007b). Acta Cryst. E63, o4132.
- Betz, R. & Klüfers, P. (2007c). Acta Cryst. E63, o4300.
- Betz, R. & Klüfers, P. (2008). Unpublished results.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Komatsu, S., Takata, T. & Endo, T. (1992). Macromolecules, 25, 7286–7293.
- Nonius (2004). COLLECT Nonius BV, Delft, The Netherlands.
- Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. (1997). Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 276, Macromolecular Crystallography, Part A, edited by C. W. Carter Jr & R. M. Sweet, pp. 307–326. New York: Academic Press.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 7–13.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807063660/lx2027sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536807063660/lx2027Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




