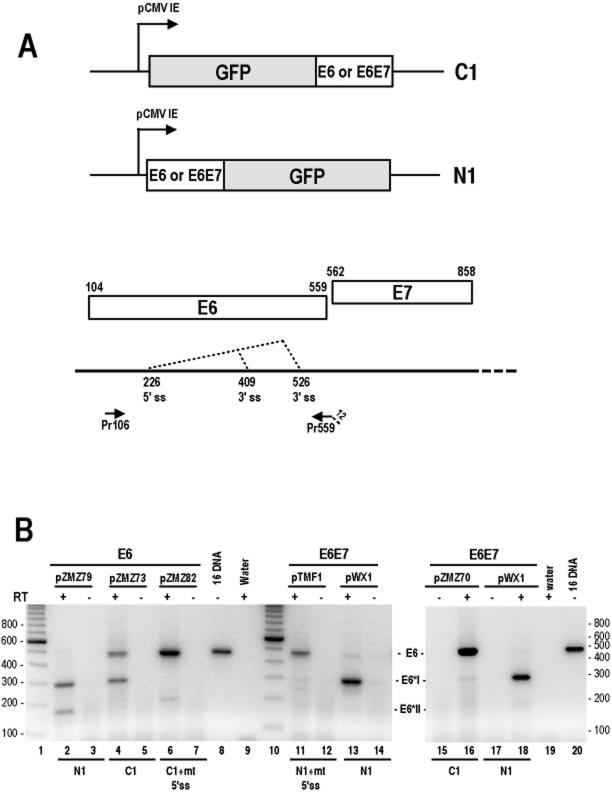
FIG. 1.
Strategy for preventing E6 pre-mRNA from splicing for the production of full-length 16E6-GFP fusions. (A) Diagram of the 16E6E7 (nt 81 to 880) or 16E6 (nt 81 to 559) coding region inserted either upstream (N1) or downstream (C1) of the GFP gene in corresponding pEGFP expression vectors. The E6 and E7 ORFs, the splicing directions of the 16E6 pre-mRNA, and a primer pair used for RT-PCR analysis are depicted below the diagram. The numbers above the E6 and E7 ORFs are start and stop codons for each ORF. ss, splice site. Drawings are not to scale. (B) Expression of 16E6 in 293 cells by transient transfection. Total cell RNA isolated from transfected cells after the removal of plasmid DNA by RNase-free DNase I treatment was examined by RT-PCR analysis with primers Pr106 and Pr559 for 16E6 RNA detection. Both plasmids pZMZ82 and pTMF1, having an mutant nt 226 5′ splice site (GU to GG), were used to transcribe unspliced E6 or E6E7 RNA as a control. The identities of the spliced and unspliced E6 RNA products are indicated between the gels. Size markers (lanes 1 and 10) from a 100-bp ladder are indicated at the left and right of the gels.