Figure 1.
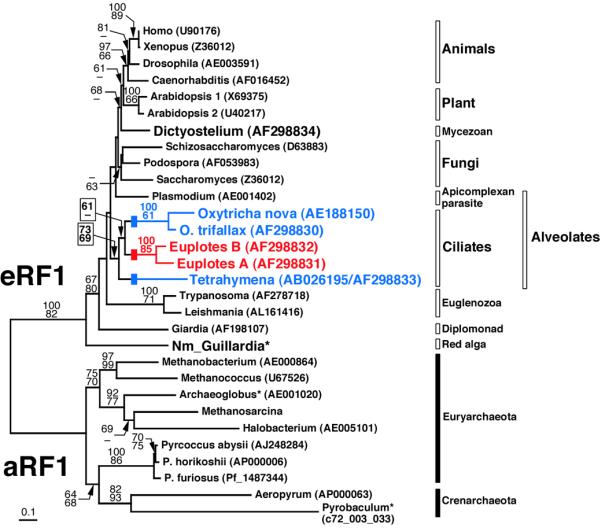
Phylogenetic tree inferred from eRF1 and aRF1 sequences. An alignment including the 15 universal code eRF1s, five variant code ciliate eRF1s and 10 aRF1s (the 15-5-10 dataset, 345 sites) was used. The tree was reconstructed from a distance matrix incorporating one invariable category and the discrete γ distribution approximated with eight variable categories, using FITCH in PHYLIP (20). Robustness of tree topologies was examined by bootstrap analysis (500 resamplings) using a distance method considering among-site substitution rates (top) and percent occurrence in 10 000 quartet puzzling trees (bottom). A dash indicates that a given node was not supported by the bootstrap score or quartet puzzling score (>60). An asterisk indicates sequences that failed in a χ2 test of amino acid composition in PUZZLE (19). The eRF1s from ciliates with variant codes are highlighted in blue (UAR for Gln) and red (UGA for Cys). Blocks on the Oxytricha, Euplotes and Tetrahymena branches indicate independent conversions from the universal code to variant codes. For the P.furiosus and Pyrobaculum aerophilum aRF1s their ORF IDs are listed, instead of GenBank accession numbers. Nm_Guillardia, Guillardia nucleomorph eRF1. The amino acid sequences of the Guillardia nucleomorph eRF1 and Methanosarcina aRF1 are available on request.
