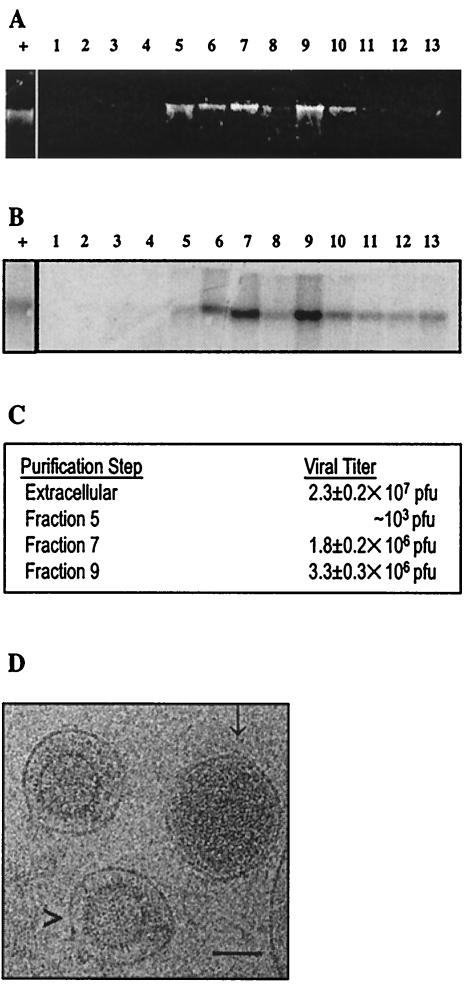
FIG. 1.
Purification of extracellular MHV68. (A) Nucleic acids extracted from MHV68 sucrose gradient fractions. Extracellular virus was purified by 5 to 55% sucrose density gradient ultracentrifugation. Numbers shown on top of the panel are fractions collected from top (1) to bottom (13) of the gradient. Nucleic acids were extracted and electrophoretically separated in a 0.75% agarose-Tris-acetate-EDTA gel. (B) Southern blot analysis of extracellular virus. DNA shown in panel A was transferred to a positively charged nylon membrane and probed with random-primed [α32P]dCTP-labeled virus-specific probe (a 760-bp PCR product of ORF67). + is intact viral genomic DNA. (C) Infectivity of sucrose gradient-purified virus. BHK cell monolayers infected with fractions 5, 7, or 9 were incubated in methylcellulose overlay medium at 37°C in 5% CO2 for 5 days, and numbers of PFU were calculated. Plaque assays were performed twice. (D) Electron cryomicrograph of MHV68 virions and enveloped capsid particles. MHV68 particles from fraction 9 were embedded in vitreous ice and recorded at 100 kV on a JEOL JEM1200 electron cryomicroscope at magnification ×30,000 at a dosage of 6 electrons/angstrom2. A representative image is shown, with putative virions (with DNA) indicated by an arrow (↓) and noninfectious enveloped particles (no DNA) indicated by an arrowhead (>). Bar, 100 nm.