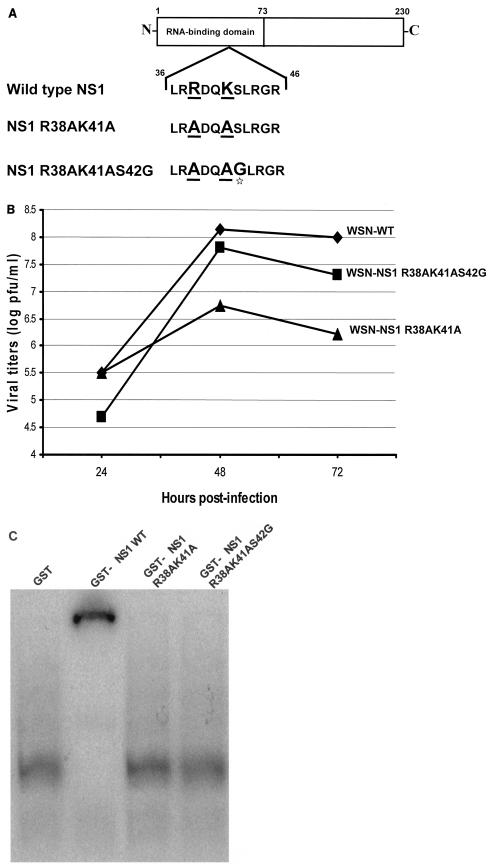
FIG. 1.
Characterization of recombinant influenza A viruses and their NS1 mutations. (A) Schematic diagram of wild-type and mutant NS1 proteins. Underlined amino acid residues were mutated to alanine. The star highlights the serine-to-glycine mutation in the NS1 R38AK41AS42G protein. (B) Multicycle growth curves of recombinant influenza A/WSN/33 viruses expressing wild-type and mutant NS1 proteins. MDCK cells were infected at an MOI of 0.001 with the different recombinant viruses. Viruses released to the supernatant were titrated at 24, 48, and 72 h postinfection by plaque assay on fresh MDCK cells. (C) Binding of GST-NS1 proteins to dsRNA in vitro. Each GST-NS1 fusion protein (0.4 μM) was incubated with 32P-radiolabeled dsRNA (10,000 cpm, 1 nM). The protein-RNA complexes were then resolved from free RNA by running them on a 6% nondenaturing polyacrylamide gel at 4°C for 3 h at 150 V in 0.045 M Tris-borate-0.001 M EDTA running buffer.