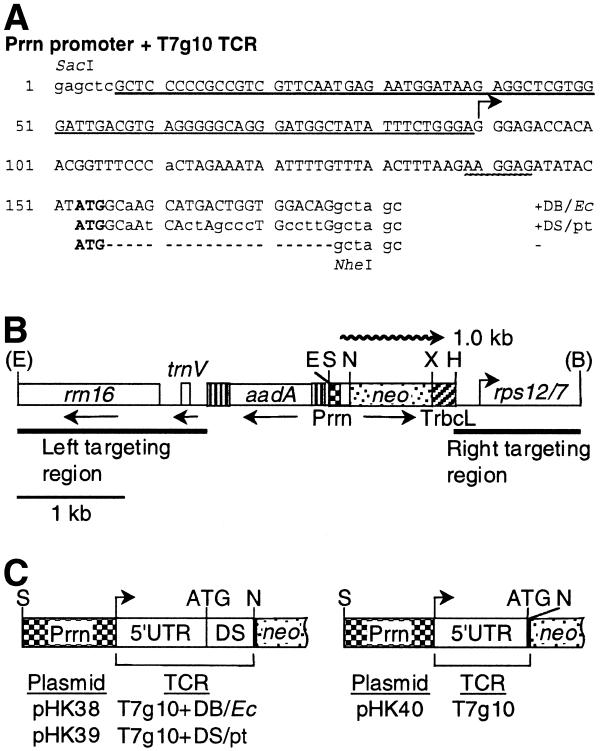
Figure 2.
Plastid vectors to compare translation efficiency from neo mRNAs with the E.coli DB and plastid DS regions. (A) DNA sequence of Prrn promoters with T7g10 leader derivatives. The Prrn promoter region is underlined; the transcription initiation site is marked by a horizontal arrow; the translation initiation codon (ATG) is in bold; the SD sequence is underlined with a wavy line. The T7g10 DB (Ec) sequence is shown on top; the sequence with the plastid DS region (pt) is duplicated in the middle; the sequence with the NheI site is at the bottom. Plastid and T7g10 sequences are in capital letters; nucleotides added or modified during construction are in lowercase; gaps are marked with dashes. (B) The plastid targeting region of the transformation vectors. The spectinomycin resistance (aadA) and neo genes and plastid genes rrn16, trnV and rps12/7 (46) are shown. The positions of the neo promoter (Prrn) and 3′-UTR (TrbcL) are also marked. The wavy line represents 1.0 kb neo mRNA. Abbreviations for restriction sites: E, EcoRI; S, SacI; N, NheI; X, XbaI; H, HindIII; B, BglII. Restriction sites removed during plasmid construction are in parentheses. (C) Listing of plasmids and the schematic map of their promoter and N-terminal coding regions. For an explanation see (B).