Abstract
In the title compound, C14H10N2O, the dihedral angle between the imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine and phenyl rings is 28.61 (4)° The molecules are connected into broad chains parallel to the a axis by weak C—H⋯O and C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds. The linking of the ribbons is provided by π–π stacking interactions between neighbouring pyridine rings, with a centroid–centroid distance of 3.7187 (7) Å.
Related literature
For general background, see Anaflous et al. (2008 ▶) and references therein. For related literature, see: Meth-Cohn & Stanforth (1991 ▶).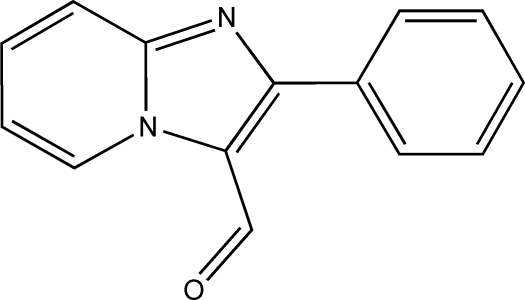
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H10N2O
M r = 222.2
Orthorhombic,
a = 13.0640 (3) Å
b = 7.4162 (2) Å
c = 21.6698 (6) Å
V = 2099.48 (9) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 120 K
0.57 × 0.40 × 0.24 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur2 diffractometer with Sapphire2 CCD detector
Absorption correction: none
25795 measured reflections
2196 independent reflections
1305 reflections with I > 3σ(I)
R int = 0.049
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.031
wR(F 2) = 0.077
S = 1.04
2196 reflections
154 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis CCD (Oxford Diffraction, 2006 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2006 ▶); data reduction: CrysAlis RED; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR2002 (Burla et al., 2003 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: JANA2000 (Petříček et al., 2000 ▶); molecular graphics: DIAMOND (Brandenburg & Putz, 2005 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: JANA2000.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011306/bg2180sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011306/bg2180Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4—H4⋯N1i | 0.96 | 2.50 | 3.4386 (18) | 165 |
| C6—H6⋯O1ii | 0.96 | 2.46 | 3.1856 (16) | 133 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 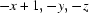 ; (ii)
; (ii) 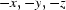 .
.
Acknowledgments
The Grant Agency of the Czech Republic is acknowledged for grant No 202/05/0757
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Functionalized imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine and imidazo[1,2-a]pyrimidine systems are of great interest due to their biological activities (Anaflous et al., 2008 and reference herein).
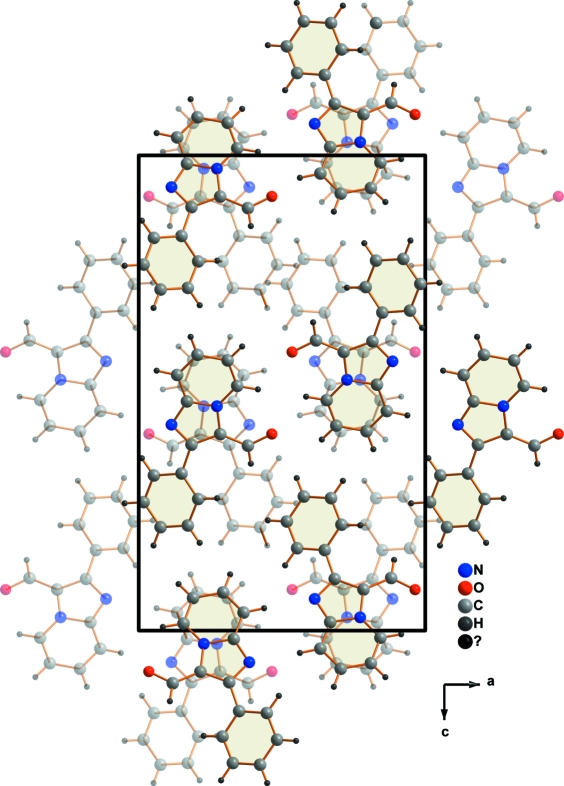
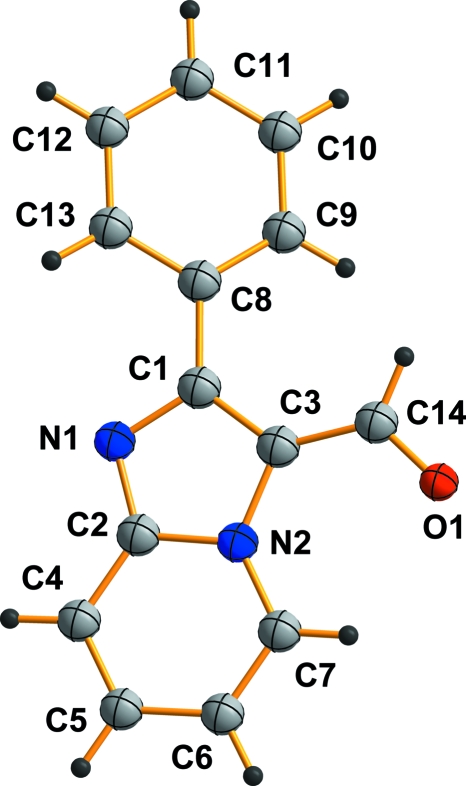
The structure of N-(2-phenylimidazo[1,2-a]pyridin-3-yl)acetamide(I) consists of isolated molecules which packing is shown in Fig. 1. The space conformation of the molecule (Fig. 2) is characterized by the dihedral angle of 28.61 (4) ° between the imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine and the phenyl rings. Weak C—H···N and C—H···O intermolecular hydrogen bonds (Table 1) connect the molecules into chains in the a direction (Fig. 3). The connection between ribbons along b (Fig. 1) is provided by π-π stacking interactions involving neighbouring pyridine rings with centroid-centroid distance 3.7187 (7) Å.
Experimental
Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-2-phenyl-3-carbaldehyde was synthesized according to the method described by Vilsmeier-Haack (Meth-Cohn & Stanforth, 1991) : i.e. to 1.9 g (26 mmol) of DMF cooled at 273 K, containing 4 g (26 mmol) of phosphorus oxychloride (POCl3), was added portionwise to 10 mmole of 2-phenyl imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine. The mixture was heated at 373 K for 1 h. The solution was then neutralized at 273 K with Na2CO3 and extracted with Dichloromethane. The organic layer was dried over sodium sulfate and dichloromethane was removed under reduced pressure. The crude product was purified on silica gel column and imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-2-phenyl-3-carbaldehyde was obtained in good yield (60%) as a white solid.
Refinement
All the hydrogens (bonded to C atoms) were discernible in difference Fourier maps but according to standard procedures for organic compounds they were constrained to ideal positions (C-H: 0.96Å). Their isotropic atomic displacement parameters were evaluated as 1.2*Ueq of the parent atom.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Packing of of Imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-2-phenyl-3-carbaldehyde viewed along the b axis. Hydrogen bonds are not indicated.
Fig. 2.
A molecule of the title compound, with 50% displacement ellispoids for non-H atoms.
Fig. 3.
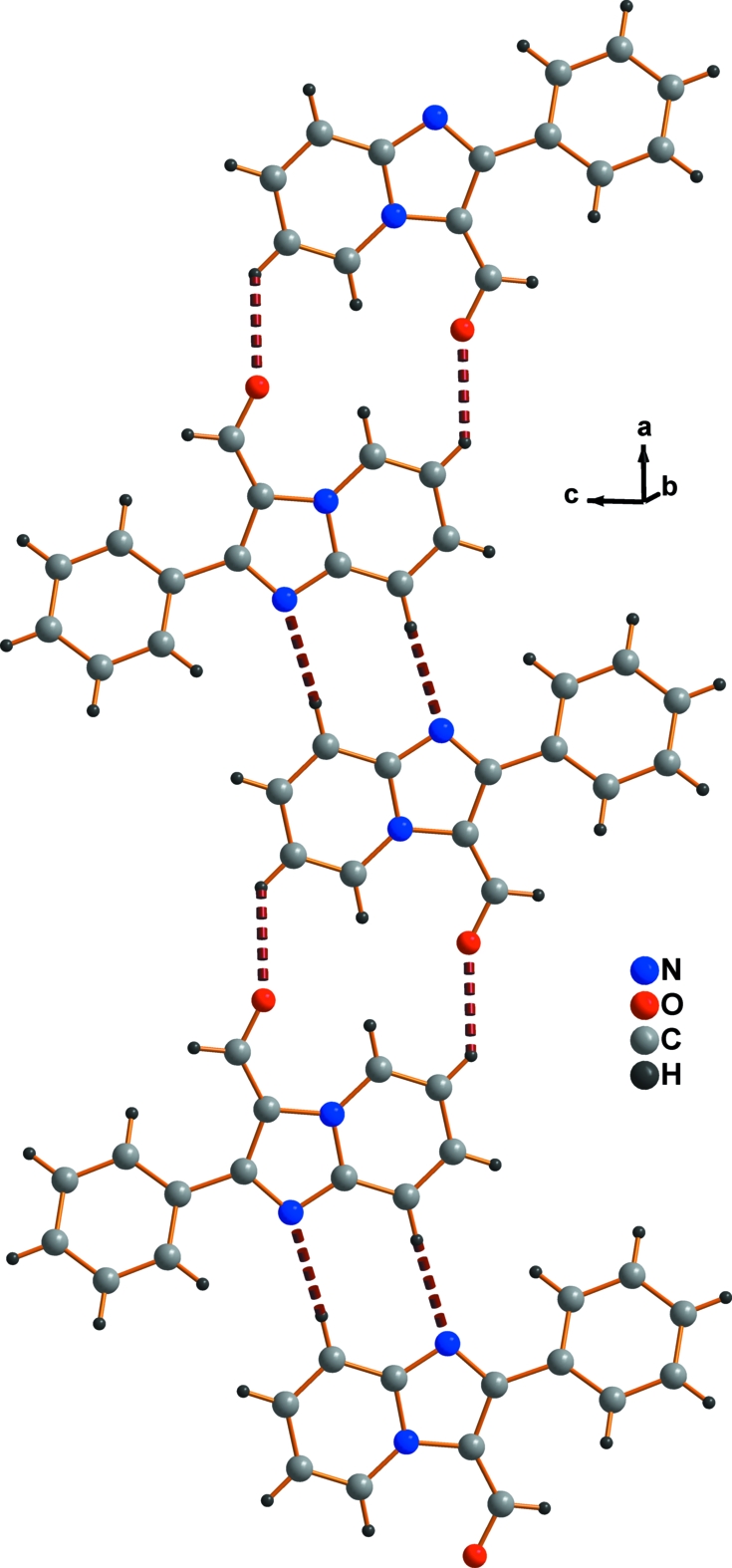
Part of a ribbon along the a axis showing intermolecular hydrogen bonds.
Crystal data
| C14H10N2O | F000 = 928 |
| Mr = 222.2 | Dx = 1.406 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, Pbca | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71069 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 8746 reflections |
| a = 13.0640 (3) Å | θ = 2.7–26.5º |
| b = 7.4162 (2) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 21.6698 (6) Å | T = 120 K |
| V = 2099.48 (9) Å3 | Prism, colourless |
| Z = 8 | 0.57 × 0.40 × 0.24 mm |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur2 diffractometer with Sapphire2 CCD detector | 2196 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: X-ray tube | 1305 reflections with I > 3σ(I) |
| Monochromator: graphite | Rint = 0.049 |
| Detector resolution: 8.3438 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 26.6º |
| T = 120 K | θmin = 3.1º |
| Rotation method data acquisition using ω scans | h = −16→16 |
| Absorption correction: none | k = −9→9 |
| 25795 measured reflections | l = −27→27 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.031 | Weighting scheme based on measured s.u.'s w = 1/[σ2(I) + 0.0016I2] |
| wR(F2) = 0.077 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.007 |
| S = 1.04 | Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3 |
| 2196 reflections | Δρmin = −0.16 e Å−3 |
| 154 parameters | Extinction correction: none |
| 36 constraints |
Special details
| Refinement. The refinement was carried out against all reflections. The conventional R-factor is always based on F. The goodness of fit as well as the weighted R-factor are based on F and F2 for refinement carried out on F and F2, respectively. The threshold expression is used only for calculating R-factors etc. and it is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement.All the H atoms were discernible in difference Fourier maps and could be refined to reasonable geometry. According to standard procedures for organic compounds the H atoms bonded to C atoms were constrained to ideal positions. The isotropic atomic displacement parameters of hydrogen atoms were evaluated as 1.2*Ueq of the parent atom.The program used for refinement, Jana2006, uses the weighting scheme based on the experimental expectations, see _refine_ls_weighting_details, that does not force S to be one. Therefore the values of S are usually larger than the ones from the SHELX program. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.38579 (8) | 0.13099 (13) | 0.06669 (5) | 0.0227 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.22707 (8) | 0.09004 (13) | 0.02784 (5) | 0.0204 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.03531 (7) | 0.19646 (11) | 0.08623 (4) | 0.0297 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.31590 (10) | 0.18666 (16) | 0.10870 (6) | 0.0208 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.33161 (10) | 0.07295 (16) | 0.01765 (6) | 0.0207 (4) | |
| C3 | 0.21543 (10) | 0.16659 (16) | 0.08658 (6) | 0.0204 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.36597 (11) | −0.00163 (16) | −0.03801 (6) | 0.0235 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.29491 (10) | −0.05736 (17) | −0.08037 (7) | 0.0243 (4) | |
| C6 | 0.18958 (10) | −0.03859 (17) | −0.06861 (6) | 0.0247 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.15617 (10) | 0.03543 (16) | −0.01503 (6) | 0.0236 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.35054 (10) | 0.25310 (16) | 0.16940 (6) | 0.0214 (4) | |
| C9 | 0.29235 (10) | 0.23521 (17) | 0.22302 (7) | 0.0238 (4) | |
| C10 | 0.32855 (11) | 0.30105 (17) | 0.27874 (7) | 0.0274 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.42372 (11) | 0.38290 (17) | 0.28223 (6) | 0.0283 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.48307 (11) | 0.39863 (17) | 0.22959 (6) | 0.0282 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.44708 (10) | 0.33402 (16) | 0.17344 (6) | 0.0242 (4) | |
| C14 | 0.11885 (10) | 0.22273 (16) | 0.11073 (7) | 0.0245 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.437543 | −0.014444 | −0.047038 | 0.0282* | |
| H5 | 0.318903 | −0.109503 | −0.118246 | 0.0292* | |
| H6 | 0.139117 | −0.077351 | −0.097954 | 0.0296* | |
| H7 | 0.084111 | 0.048834 | −0.007645 | 0.0283* | |
| H9 | 0.226757 | 0.177012 | 0.221555 | 0.0286* | |
| H10 | 0.287357 | 0.289867 | 0.315233 | 0.0329* | |
| H11 | 0.448433 | 0.4285 | 0.320918 | 0.0339* | |
| H12 | 0.549259 | 0.454408 | 0.232038 | 0.0339* | |
| H13 | 0.489068 | 0.345338 | 0.137292 | 0.0291* | |
| H14 | 0.108688 | 0.287015 | 0.148695 | 0.0294* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0207 (6) | 0.0225 (5) | 0.0249 (6) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0017 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0196 (6) | 0.0177 (5) | 0.0239 (6) | −0.0005 (5) | −0.0001 (5) | 0.0031 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0200 (6) | 0.0315 (5) | 0.0376 (6) | 0.0000 (4) | −0.0002 (5) | 0.0024 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0221 (7) | 0.0149 (7) | 0.0255 (8) | 0.0007 (6) | 0.0019 (6) | 0.0052 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0192 (7) | 0.0170 (6) | 0.0259 (8) | −0.0002 (6) | 0.0015 (6) | 0.0051 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0211 (7) | 0.0179 (6) | 0.0223 (7) | −0.0008 (6) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0026 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0219 (8) | 0.0224 (7) | 0.0263 (8) | −0.0005 (6) | 0.0024 (6) | 0.0027 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0281 (8) | 0.0201 (7) | 0.0248 (8) | −0.0015 (6) | 0.0020 (6) | 0.0031 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0245 (8) | 0.0220 (7) | 0.0275 (8) | −0.0044 (6) | −0.0037 (6) | 0.0023 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0194 (8) | 0.0225 (7) | 0.0289 (8) | −0.0025 (6) | −0.0031 (6) | 0.0043 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0228 (8) | 0.0155 (6) | 0.0260 (8) | 0.0027 (6) | −0.0010 (6) | 0.0032 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0216 (8) | 0.0212 (7) | 0.0288 (8) | −0.0003 (6) | −0.0001 (7) | 0.0034 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0313 (8) | 0.0267 (7) | 0.0242 (8) | 0.0049 (7) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0034 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0330 (8) | 0.0255 (7) | 0.0263 (8) | 0.0053 (7) | −0.0057 (7) | −0.0006 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0266 (8) | 0.0242 (7) | 0.0339 (8) | −0.0021 (6) | −0.0043 (7) | 0.0013 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0243 (8) | 0.0222 (7) | 0.0263 (8) | 0.0009 (6) | 0.0007 (6) | 0.0032 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0262 (8) | 0.0201 (7) | 0.0271 (8) | 0.0008 (7) | 0.0032 (7) | 0.0041 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| N1—C1 | 1.3537 (16) | C6—H6 | 0.9600 |
| N1—C2 | 1.3475 (16) | C7—H7 | 0.9600 |
| N2—C2 | 1.3893 (16) | C8—C9 | 1.3949 (19) |
| N2—C3 | 1.4020 (17) | C8—C13 | 1.3994 (18) |
| N2—C7 | 1.3731 (17) | C9—C10 | 1.386 (2) |
| O1—C14 | 1.2293 (16) | C9—H9 | 0.9600 |
| C1—C3 | 1.4052 (18) | C10—C11 | 1.3857 (19) |
| C1—C8 | 1.4758 (18) | C10—H10 | 0.9600 |
| C2—C4 | 1.4008 (18) | C11—C12 | 1.3840 (19) |
| C3—C14 | 1.4279 (18) | C11—H11 | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3693 (19) | C12—C13 | 1.3897 (19) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9600 | C12—H12 | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.4063 (18) | C13—H13 | 0.9600 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9600 | C14—H14 | 0.9600 |
| C6—C7 | 1.3564 (19) | ||
| C1—N1—C2 | 105.87 (10) | N2—C7—H7 | 121.20 |
| C2—N2—C3 | 106.74 (10) | C6—C7—H7 | 120.02 |
| C2—N2—C7 | 121.92 (11) | C1—C8—C9 | 122.93 (12) |
| C3—N2—C7 | 131.34 (11) | C1—C8—C13 | 118.38 (12) |
| N1—C1—C3 | 111.62 (11) | C9—C8—C13 | 118.67 (12) |
| N1—C1—C8 | 119.62 (11) | C8—C9—C10 | 120.43 (12) |
| C3—C1—C8 | 128.74 (12) | C8—C9—H9 | 120.11 |
| N1—C2—N2 | 111.21 (11) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.46 |
| N1—C2—C4 | 129.56 (12) | C9—C10—C11 | 120.53 (13) |
| N2—C2—C4 | 119.21 (11) | C9—C10—H10 | 119.74 |
| N2—C3—C1 | 104.54 (11) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.73 |
| N2—C3—C14 | 123.14 (12) | C10—C11—C12 | 119.65 (13) |
| C1—C3—C14 | 132.02 (12) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.24 |
| C2—C4—C5 | 118.63 (12) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.11 |
| C2—C4—H4 | 121.78 | C11—C12—C13 | 120.19 (12) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.59 | C11—C12—H12 | 119.70 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.80 (13) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.11 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 118.26 | C8—C13—C12 | 120.50 (12) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.94 | C8—C13—H13 | 120.09 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.66 (12) | C12—C13—H13 | 119.40 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 121.49 | O1—C14—C3 | 125.44 (13) |
| C7—C6—H6 | 117.85 | O1—C14—H14 | 109.03 |
| N2—C7—C6 | 118.78 (12) | C3—C14—H14 | 125.53 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4···N1i | 0.96 | 2.50 | 3.4386 (18) | 165 |
| C6—H6···O1ii | 0.96 | 2.46 | 3.1856 (16) | 133 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z; (ii) −x, −y, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BG2180).
References
- Anaflous, A., Albay, H., Benchat, N., El Bali, B., Dusek, M. & Fejfarova, K. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Brandenburg, K. & Putz, H. (2005). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Postfach 1251, D-53002 Bonn, Germany.
- Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Carrozzini, B., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (2003). J. Appl. Cryst.36, 1103.
- Meth-Cohn, O. & Stanforth, S. P. (1991). Comp. Org. Synth.2, 777–794.
- Oxford Diffraction (2006). CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abingdon, Oxfordshire, England.
- Petříček, V., Dušek, M. & Palatinus, L. (2000). JANA2000 Institute of Physics, Prague, Czech Republic.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011306/bg2180sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808011306/bg2180Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report