Figure 1.
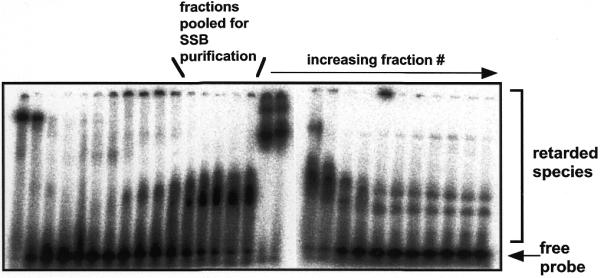
Detection of a ssDNA binding activity in extracts of S.solfataricus fractionated by anion-exchange chromatography. Aliquots (1 µl) of protein eluting from a SP-Sepharose column developed with a gradient of increasing NaCl were incubated with a ssDNA probe (radioactively labelled 18mer oligonucleotide) in binding buffer containing a large excess of unlabelled calf thymus duplex DNA, prior to detection of retarded species by EMSA. The fractions indicated were pooled and purified through a further two chromatography steps, yielding essentially homogeneous native Sulfolobus SSB protein (Fig. 3). The strongly retarded species apparent in fractions later than those collected are due to the presence of an abundant dsDNA binding protein, Sso10b (data not shown).
