Abstract
A new monoclinic polymorphic form of the title compound, [Cu(HCO2)2(C14H12N2)(H2O)], is described. It differs from the first orthorhombic polymorph [Pan, Lin & Zheng (2005 ▶). Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct. 220, 495–496] in the deviation of the Cu atom relative to the plane of the 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline (dmp) ligand. In the present structure, the Cu atom is shifted from the mean plane of the dmp ligand by only 0.005 (1) Å, compared with 0.318 (6) Å in the orthorhombic form. Hydrogen-bonding and π–π stacking interactions (mean interplanar distance of 3.59 Å in the title compound) in the two different polymorphs are both essential to the supramolecular assembly.
Related literature
For the orthorhombic polymorph, see: Pan et al. (2005 ▶).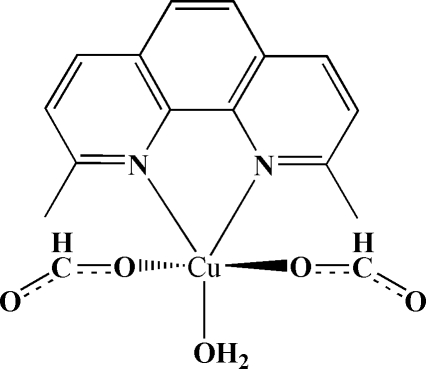
Experimental
Crystal data
[Cu(HCO2)2(C14H12N2)(H2O)]
M r = 379.85
Monoclinic,
a = 10.669 (2) Å
b = 7.7677 (16) Å
c = 19.338 (4) Å
β = 94.22 (3)°
V = 1598.3 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.40 mm−1
T = 295 (2) K
0.26 × 0.17 × 0.09 mm
Data collection
Bruker P4 diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (XSCANS; Siemens, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.749, T max = 0.879
15099 measured reflections
3632 independent reflections
3202 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.019
3 standard reflections every 97 reflections intensity decay: none
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.026
wR(F 2) = 0.072
S = 1.06
3632 reflections
219 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.35 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3
Data collection: XSCANS (Siemens, 1996 ▶); cell refinement: XSCANS; data reduction: XSCANS; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXL97; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808022812/fj2128sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808022812/fj2128Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected geometric parameters (Å, °).
| Cu—O1 | 1.9450 (12) |
| Cu—O3 | 1.9546 (12) |
| Cu—O5 | 1.9726 (12) |
| Cu—N1 | 2.0328 (13) |
| Cu—N2 | 2.2801 (15) |
| O1—Cu—O3 | 95.53 (6) |
| O1—Cu—O5 | 87.40 (6) |
| O1—Cu—N1 | 174.06 (6) |
| O1—Cu—N2 | 107.40 (6) |
| O3—Cu—O5 | 167.05 (6) |
| O3—Cu—N1 | 86.33 (5) |
| O3—Cu—N2 | 95.28 (6) |
| O5—Cu—N1 | 89.57 (5) |
| O5—Cu—N2 | 95.87 (5) |
| N1—Cu—N2 | 77.98 (6) |
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O5—H5C⋯O2i | 0.88 | 1.86 | 2.714 (2) | 166 |
| O5—H5B⋯O4ii | 0.89 | 1.72 | 2.605 (2) | 175 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 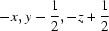 ; (ii)
; (ii) 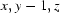 .
.
Acknowledgments
This project was sponsored by the K. C. Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University, the Expert Project of Key Basic Research of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (grant No. 2003CCA00800), and the Ningbo Municipal Natural Science Foundation (grant No. 2006 A610061).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
We reported a structure of the copper-dmp complex aqua-(2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline-κ2N:N')-diromato-copper(II) previously, which crystallizes in space group Pna21 (Pan, et al.,2005). On repeating the experiment recently, to our surprise, we found a new polyporph, (I), that had crystallized in the space group P21/c.
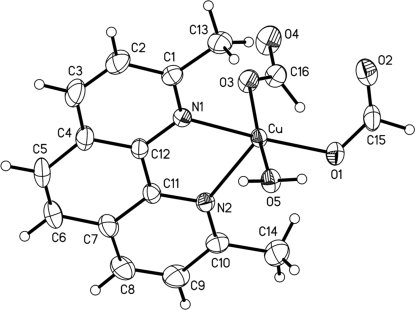
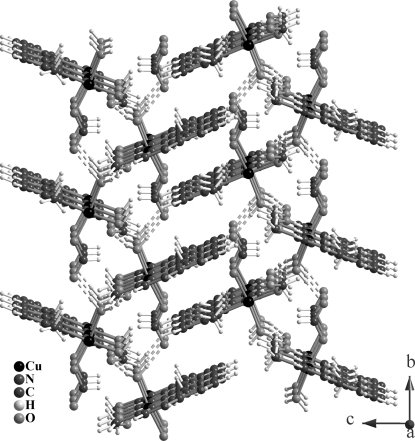
The crystal structure of the title compound is very similar to the previously reported complex, built up by the [Cu(dmp)(H2O)(HCOO)2] complex molecules. The Cu atoms are each square pyramidally coordinated by two N atoms of one dmp ligand, three O atoms of two formate anions and one water molecule with the N2 atom of the dmp ligand at the apical position. The apical and basal Cu—N bond distances are 2.280 (1) and 2.033 (2) Å, respectively. The Cu—O bond distances to the formate anions are 1.945 (1) and 1.955 (1) Å, slightly longer than that to the water molecule (1.973 (1) Å). Suggesting that the formate anions possess better coordinating capability to the water molecule in the structure, which also show no significant difference from the isomer crystal structure that reported by us. The Cu atom is shifted by 0.153 (1) Å from the equatorial plane through N1, O1, O3 and O5 atoms towards the apical N2 atom. Through the intermolecular hydrogen bond the complex molecules are link into double chains with the chelating dmp ligands extending parallelly on one side along [010]. The substituted phenanthroline ligands of one double chain protrude into the grooves between adjacent aromatic planes of the neighboring double chain, yielding two-dimensional layers parallel to (100). It is found that the assembly of the double chains is due to interchain π-π stacking interactions between the dmp ligands (mean interplanar distance: 3.59 Å).
Experimental
Dropwise addition of 2.0 ml (1.0 M) Na2CO3 to an aqueous solution of 0.075 g (0.442 mmol) CuCl2.2H2O in 5.0 ml H2O yielded pale blue deposit, which was separated by centrifugation and washed with doubly distilled water until no Cl- anions are detectable in the supernatant. The precipitate was then added to a solution of 0.100 g (0.442 mmol) 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline in a mixed solvent consisting of 15 ml H2O and 15 ml me thanol. To the mixture 1.77 ml (1.0 M) formic acid was dropped and the precipitate was slowly dissolved under continuous stirring. The resulting blue solution was allowed to stand at room temperature, and slow evaporation for 10 days afforded blue plate crystals.
Refinement
H atoms attached to C atoms of the dmp ligand were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model, with C—H = 0.93 and 0.96 Å, and Uiso(H) values set at 1.2 Ueq(C) and 1.5 Ueq(C), respectively. The H atoms of the water molecule and formate anions were located from difference Fourier maps.
Figures
Fig. 1.
ORTEP view of the title compound. The displacement ellipsoids are drawn at 40% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A perspective view of the crystal structure of (I), with hydrogen bonds shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| [Cu(HCO2)2(C14H12N2)(H2O)] | F000 = 780 |
| Mr = 379.85 | Dx = 1.579 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 25 reflections |
| a = 10.669 (2) Å | θ = 5.0–12.5º |
| b = 7.7677 (16) Å | µ = 1.40 mm−1 |
| c = 19.338 (4) Å | T = 295 (2) K |
| β = 94.22 (3)º | Plate, blue |
| V = 1598.3 (6) Å3 | 0.26 × 0.17 × 0.09 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker P4 diffractometer | Rint = 0.019 |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | θmax = 27.5º |
| Monochromator: graphite | θmin = 3.3º |
| T = 295(2) K | h = −13→13 |
| θ/2θ scans | k = −10→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan(XSCANS; Siemens, 1996) | l = −24→25 |
| Tmin = 0.749, Tmax = 0.879 | 3 standard reflections |
| 15099 measured reflections | every 97 reflections |
| 3632 independent reflections | intensity decay: none |
| 3202 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.026 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.072 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0413P)2 + 0.5201P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.06 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 3632 reflections | Δρmax = 0.35 e Å−3 |
| 219 parameters | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction correction: none |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cu | 0.209657 (18) | 0.90493 (2) | 0.156116 (9) | 0.02440 (7) | |
| N1 | 0.21922 (12) | 0.80402 (17) | 0.05966 (6) | 0.0257 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.42113 (13) | 0.89494 (17) | 0.14606 (7) | 0.0275 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.11886 (17) | 0.7632 (2) | 0.01841 (9) | 0.0325 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.1317 (2) | 0.6999 (3) | −0.04910 (10) | 0.0472 (5) | |
| H2A | 0.0605 | 0.6741 | −0.0778 | 0.057* | |
| C3 | 0.2471 (2) | 0.6765 (3) | −0.07224 (10) | 0.0508 (5) | |
| H3A | 0.2552 | 0.6332 | −0.1165 | 0.061* | |
| C4 | 0.35505 (19) | 0.7178 (3) | −0.02912 (9) | 0.0393 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.4803 (2) | 0.6986 (3) | −0.04949 (11) | 0.0541 (6) | |
| H5A | 0.4929 | 0.6540 | −0.0931 | 0.065* | |
| C6 | 0.5804 (2) | 0.7435 (3) | −0.00711 (11) | 0.0537 (6) | |
| H6A | 0.6609 | 0.7298 | −0.0217 | 0.064* | |
| C7 | 0.56433 (17) | 0.8120 (3) | 0.05998 (10) | 0.0397 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.66470 (19) | 0.8661 (3) | 0.10598 (12) | 0.0511 (5) | |
| H8A | 0.7468 | 0.8577 | 0.0931 | 0.061* | |
| C9 | 0.64241 (19) | 0.9302 (3) | 0.16884 (12) | 0.0478 (5) | |
| H9A | 0.7091 | 0.9659 | 0.1992 | 0.057* | |
| C10 | 0.51845 (17) | 0.9430 (2) | 0.18838 (9) | 0.0350 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.44274 (15) | 0.8321 (2) | 0.08260 (8) | 0.0289 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.33615 (16) | 0.7831 (2) | 0.03694 (8) | 0.0281 (3) | |
| C13 | −0.00801 (18) | 0.7856 (3) | 0.04536 (10) | 0.0438 (4) | |
| H13A | −0.0302 | 0.6831 | 0.0694 | 0.066* | |
| H13B | −0.0691 | 0.8066 | 0.0073 | 0.066* | |
| H13C | −0.0062 | 0.8816 | 0.0767 | 0.066* | |
| C14 | 0.4920 (2) | 1.0068 (3) | 0.25888 (10) | 0.0537 (6) | |
| H14A | 0.4243 | 1.0884 | 0.2547 | 0.081* | |
| H14B | 0.5659 | 1.0614 | 0.2802 | 0.081* | |
| H14C | 0.4691 | 0.9116 | 0.2870 | 0.081* | |
| O1 | 0.18364 (13) | 0.98991 (18) | 0.24857 (6) | 0.0408 (3) | |
| O2 | −0.02000 (15) | 1.0452 (3) | 0.22488 (8) | 0.0613 (4) | |
| C15 | 0.0760 (2) | 1.0407 (3) | 0.26275 (10) | 0.0471 (5) | |
| O3 | 0.18495 (13) | 1.12747 (15) | 0.10994 (6) | 0.0365 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.18327 (18) | 1.41073 (16) | 0.10823 (8) | 0.0530 (4) | |
| C16 | 0.19793 (18) | 1.2723 (2) | 0.13792 (9) | 0.0360 (4) | |
| O5 | 0.19568 (12) | 0.67025 (15) | 0.19376 (6) | 0.0344 (3) | |
| H5B | 0.1958 | 0.5834 | 0.1636 | 0.051* | |
| H5C | 0.1416 | 0.6452 | 0.2242 | 0.054* | |
| H15 | 0.0751 | 1.0904 | 0.3111 | 0.052* | |
| H16 | 0.2383 | 1.2705 | 0.1852 | 0.049* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cu | 0.02683 (11) | 0.02277 (11) | 0.02410 (11) | 0.00161 (7) | 0.00524 (7) | −0.00126 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0280 (7) | 0.0227 (6) | 0.0263 (6) | −0.0003 (5) | 0.0021 (5) | −0.0001 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0267 (7) | 0.0283 (7) | 0.0276 (6) | −0.0012 (5) | 0.0032 (5) | 0.0011 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0353 (9) | 0.0304 (8) | 0.0313 (8) | −0.0023 (7) | −0.0011 (7) | −0.0003 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0495 (12) | 0.0554 (12) | 0.0350 (9) | −0.0055 (10) | −0.0086 (8) | −0.0096 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0627 (14) | 0.0601 (13) | 0.0297 (9) | −0.0010 (11) | 0.0040 (9) | −0.0158 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0467 (11) | 0.0421 (10) | 0.0300 (8) | 0.0022 (8) | 0.0093 (7) | −0.0060 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0587 (14) | 0.0690 (15) | 0.0373 (10) | 0.0073 (11) | 0.0227 (9) | −0.0110 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0430 (12) | 0.0737 (15) | 0.0474 (11) | 0.0080 (10) | 0.0234 (9) | −0.0016 (11) |
| C7 | 0.0319 (9) | 0.0479 (11) | 0.0408 (9) | 0.0023 (8) | 0.0126 (7) | 0.0052 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0246 (9) | 0.0722 (14) | 0.0575 (12) | −0.0005 (9) | 0.0102 (8) | 0.0079 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0306 (10) | 0.0592 (13) | 0.0526 (12) | −0.0096 (9) | −0.0033 (8) | 0.0047 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0323 (9) | 0.0346 (9) | 0.0374 (9) | −0.0041 (7) | −0.0018 (7) | 0.0021 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0292 (8) | 0.0288 (8) | 0.0295 (7) | 0.0007 (6) | 0.0077 (6) | 0.0020 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0327 (8) | 0.0264 (7) | 0.0258 (7) | 0.0020 (6) | 0.0070 (6) | 0.0006 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0308 (9) | 0.0564 (12) | 0.0434 (10) | −0.0056 (9) | −0.0033 (8) | 0.0005 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0484 (12) | 0.0687 (15) | 0.0426 (11) | −0.0057 (11) | −0.0066 (9) | −0.0160 (11) |
| O1 | 0.0475 (8) | 0.0463 (8) | 0.0293 (6) | 0.0104 (6) | 0.0073 (5) | −0.0055 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0465 (9) | 0.0904 (13) | 0.0485 (8) | 0.0135 (9) | 0.0128 (7) | −0.0072 (9) |
| C15 | 0.0577 (13) | 0.0534 (12) | 0.0319 (9) | 0.0127 (10) | 0.0159 (9) | −0.0061 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0529 (8) | 0.0249 (6) | 0.0319 (6) | 0.0037 (5) | 0.0045 (5) | 0.0000 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0859 (12) | 0.0259 (7) | 0.0479 (8) | 0.0012 (7) | 0.0098 (8) | 0.0004 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0443 (10) | 0.0292 (9) | 0.0346 (8) | −0.0012 (7) | 0.0028 (7) | −0.0013 (7) |
| O5 | 0.0415 (7) | 0.0271 (6) | 0.0359 (6) | −0.0028 (5) | 0.0122 (5) | 0.0032 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cu—O1 | 1.9450 (12) | C7—C11 | 1.408 (2) |
| Cu—O3 | 1.9546 (12) | C8—C9 | 1.351 (3) |
| Cu—O5 | 1.9726 (12) | C8—H8A | 0.9300 |
| Cu—N1 | 2.0328 (13) | C9—C10 | 1.405 (3) |
| Cu—N2 | 2.2801 (15) | C9—H9A | 0.9300 |
| N1—C1 | 1.326 (2) | C10—C14 | 1.497 (3) |
| N1—C12 | 1.363 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.439 (2) |
| N2—C10 | 1.327 (2) | C13—H13A | 0.9600 |
| N2—C11 | 1.356 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.411 (2) | C13—H13C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C13 | 1.496 (3) | C14—H14A | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.353 (3) | C14—H14B | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | C14—H14C | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.408 (3) | O1—C15 | 1.264 (2) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9300 | O2—C15 | 1.215 (3) |
| C4—C12 | 1.403 (2) | C15—H15 | 1.0122 |
| C4—C5 | 1.429 (3) | O3—C16 | 1.252 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.343 (3) | O4—C16 | 1.223 (2) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9300 | C16—H16 | 0.9821 |
| C6—C7 | 1.424 (3) | O5—H5B | 0.8914 |
| C6—H6A | 0.9300 | O5—H5C | 0.8760 |
| C7—C8 | 1.405 (3) | ||
| O1—Cu—O3 | 95.53 (6) | C9—C8—H8A | 119.9 |
| O1—Cu—O5 | 87.40 (6) | C7—C8—H8A | 119.9 |
| O1—Cu—N1 | 174.06 (6) | C8—C9—C10 | 119.97 (19) |
| O1—Cu—N2 | 107.40 (6) | C8—C9—H9A | 120.0 |
| O3—Cu—O5 | 167.05 (6) | C10—C9—H9A | 120.0 |
| O3—Cu—N1 | 86.33 (5) | N2—C10—C9 | 121.54 (18) |
| O3—Cu—N2 | 95.28 (6) | N2—C10—C14 | 117.62 (17) |
| O5—Cu—N1 | 89.57 (5) | C9—C10—C14 | 120.81 (18) |
| O5—Cu—N2 | 95.87 (5) | N2—C11—C7 | 122.89 (16) |
| N1—Cu—N2 | 77.98 (6) | N2—C11—C12 | 118.11 (14) |
| C1—N1—C12 | 119.71 (14) | C7—C11—C12 | 119.01 (15) |
| C1—N1—Cu | 123.47 (11) | N1—C12—C4 | 122.22 (16) |
| C12—N1—Cu | 116.80 (11) | N1—C12—C11 | 118.15 (14) |
| C10—N2—C11 | 118.80 (15) | C4—C12—C11 | 119.63 (16) |
| C10—N2—Cu | 132.20 (12) | C1—C13—H13A | 109.5 |
| C11—N2—Cu | 108.95 (11) | C1—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 120.71 (17) | H13A—C13—H13B | 109.5 |
| N1—C1—C13 | 118.29 (15) | C1—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C13 | 121.00 (17) | H13A—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.38 (18) | H13B—C13—H13C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 119.8 | C10—C14—H14A | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 119.8 | C10—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.86 (17) | H14A—C14—H14B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 120.1 | C10—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 120.1 | H14A—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C12—C4—C3 | 117.10 (18) | H14B—C14—H14C | 109.5 |
| C12—C4—C5 | 119.28 (18) | C15—O1—Cu | 119.93 (13) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 123.61 (18) | O2—C15—O1 | 128.13 (18) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.48 (18) | O2—C15—H15 | 118.8 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.3 | O1—C15—H15 | 112.9 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.3 | C16—O3—Cu | 126.20 (12) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 120.61 (18) | O4—C16—O3 | 125.51 (17) |
| C5—C6—H6A | 119.7 | O4—C16—H16 | 118.8 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 119.7 | O3—C16—H16 | 114.6 |
| C8—C7—C11 | 116.55 (17) | Cu—O5—H5B | 117.0 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 123.44 (18) | Cu—O5—H5C | 121.6 |
| C11—C7—C6 | 119.99 (19) | H5B—O5—H5C | 107.7 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 120.23 (18) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O5—H5C···O2i | 0.88 | 1.86 | 2.714 (2) | 166 |
| O5—H5B···O4ii | 0.89 | 1.72 | 2.605 (2) | 175 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) x, y−1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: FJ2128).
References
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808022812/fj2128sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536808022812/fj2128Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report