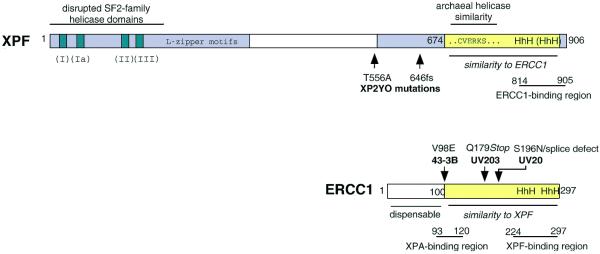
Figure 5.
Domain structure of XPF and ERCC1. Human XPF and ERCC1 are shown as examples. XPF consists of two conserved areas (grey) separated by a less conserved region in the middle. The N-terminal area includes homology to SF2-family helicase domains I–III, and a predicted leucine zipper region. In the C-terminal region there is an area of similarity (yellow) to ERCC1. Sequence details for this region are shown in Figure 6. Part of this region shows a high similarity to a region near the C-terminus of archaeal helicases (36). In ERCC1, approximately the first 100 amino acids are dispensable and the remainder of the protein (yellow) shows similarity to XPF. Positions of known mutations in the ERCC1 and XPF cells used in this study are indicated; no mutation has been reported for UV41. The ERCC1- and XPF-binding regions are from de Laat et al. (31) and the XPA-binding region is from Li et al. (44).