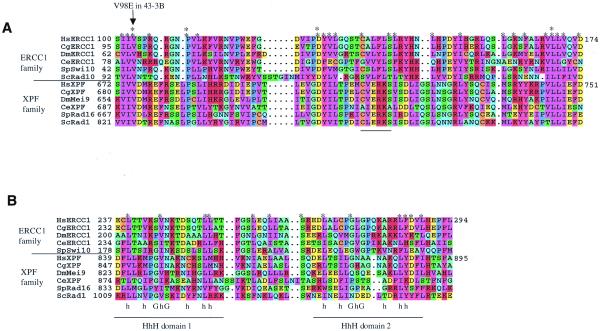
Figure 6.
Regions of similarity between XPF and ERCC1. Results of a Clustal X alignment performed between XPF and ERCC1 family members starting at the positions numbered in (A). This comparison used sequences from Homo sapiens (Hs), the Chinese hamster Cricetulus griseus (Cg), the fruitfly Drosophila melanogaster (Dm), the nematode C.elegans, the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe, and the budding yeast S.cerevisiae. Residues were coloured in MacBoxshade using similarity groupings as follows: {K, R, H}, {D, E}, {I, L, V, M}, {F, Y, W}, {Q, N}, {G, A}, {S, T}, {P} and {C}. Asterisks indicate positions highly conserved throughout the ERCC1 and XPF family alignment, and double asterisks highlight residues identical throughout both families. (A) The area of proteins most conserved between the two families. (B) The region including the HhH domains, along with the consensus sequence for HhH domains (42), where h represents a hydrophobic residue. Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rad10 does not contain this region and so is absent from this portion of the alignment.