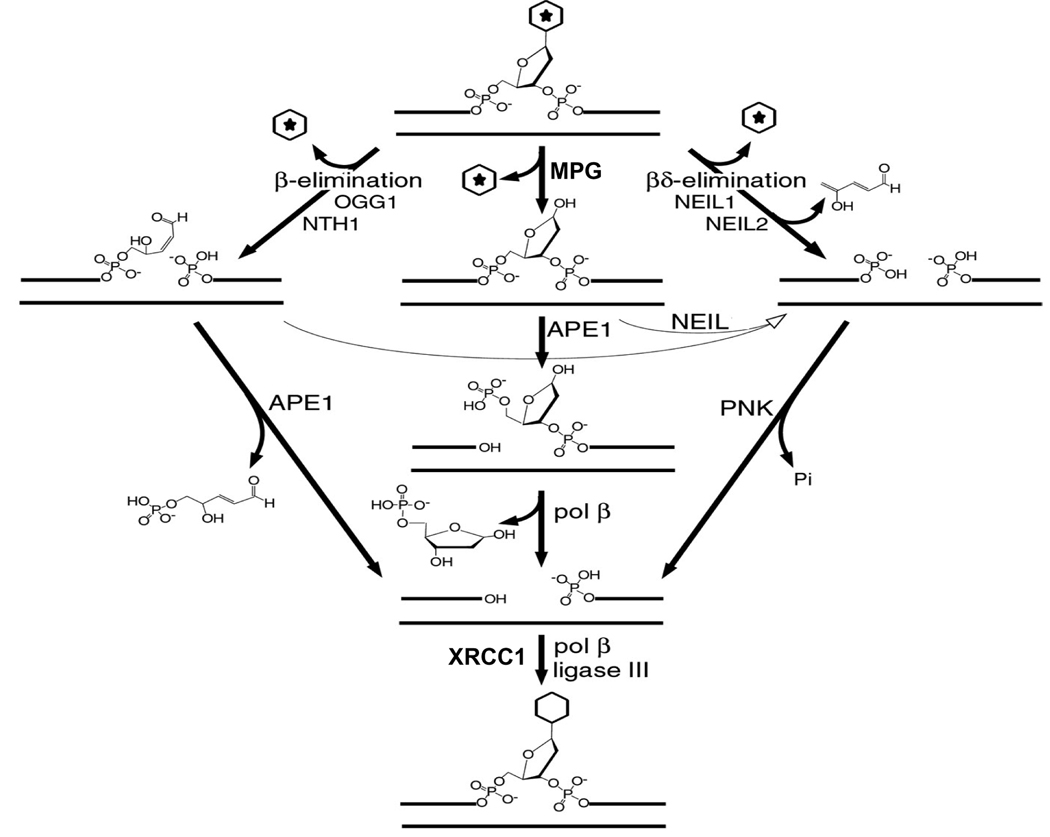
Figure 4.
Base excision repair, showing the importance of the AP lyase activities of the DNA glycosylases that act on a variety of base lesions. Under normal conditions, glycosylases that lack an AP lyase activity (e.g. MPG) or possess a β-elimination lyase activity (e.g. OGG1 and NTH1) depend on APE1 for the subsequent processing of the abasic sites. Glycosylases with a lyase acting by β.δ-elimination, such as NEIL1 and NEIL2, rely on PNK to remove the 3’-phosphate group. However, the lyase activity of NEIL1 and NEIL2 can also act on the intermediates generated by the other classes of DNA glycosylase, and therefore provide the basis for an alternative APE-independent repair pathway for these glycosylases. (Adapted from reference [30]).