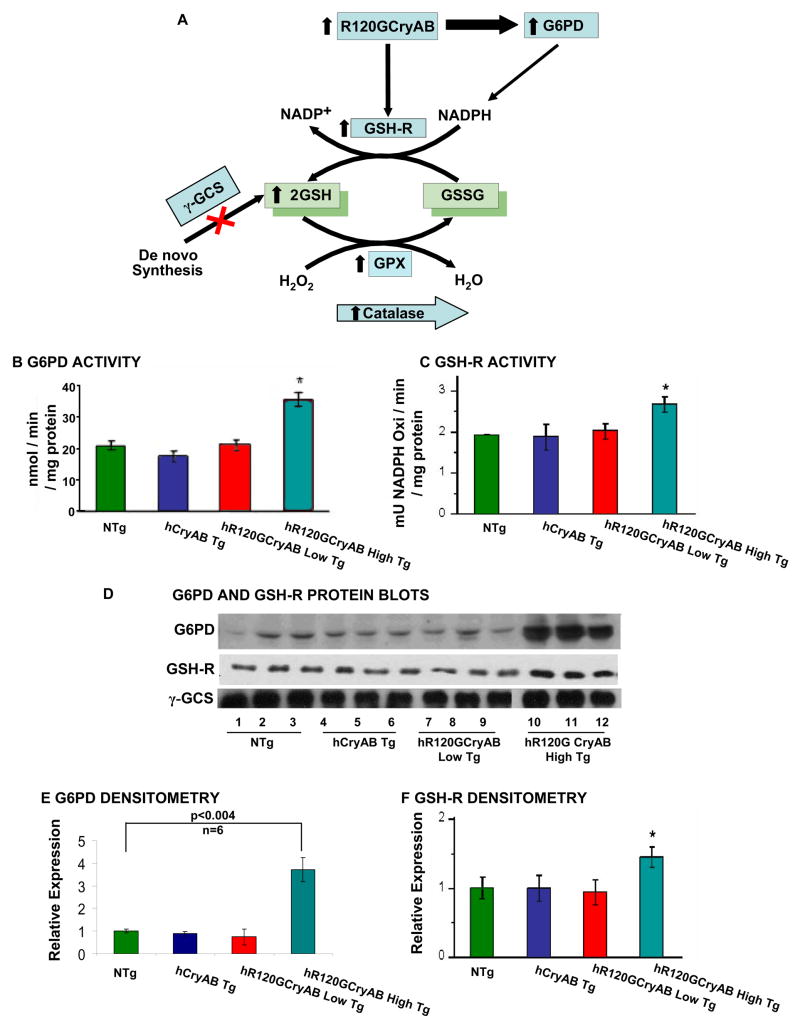
Figure 4. R120GCryAB Overexpression Enhances Antioxidative Enzymatic and GSH Recycling Pathways.
(A) The schematic diagram illustrates the effects of hR120GCryAB expression on upregulation of Hsp25 and G6PD, the first and rate-limiting enzyme of the anaerobic pentose phosphate pathway and major source of reducing equivalents in the form of NADPH. Reduced glutathione (GSH) is generated by increased activity of glutathione reductase from recycling and not from de novo synthesis. Catalase and glutathione peroxidase (which consumes GSH) catalyze the conversion of reactive oxygen species such as hydrogen peroxide to H2O.
(B) Human hR120GCryAB causes modest increase in G6PD enzyme activity in 6 month old hR120GCryAB High Tg expressors compared with the control groups.
(C) Glutathione reductase, which catalyses the recycling of GSSG to GSH, exhibits increased activity and expression in heart homogenates with hR120GCryAB High Tg expression at 6 months (*p<0.05).
(D) Representative Western blot analysis of G6PD, GSH-R and α-GCS protein expression in 6 month old hR120GCryAB High Tg animals.
(E, F) Densitometry analysis of the protein bands expressed in arbitrary units shows ~ 4 fold increase of G6PD (n=6) and ~40 % increase of GSH-R in the transgenic hearts with hR120GCryAB High expression compared to NTg, respectively (*p<0.05).