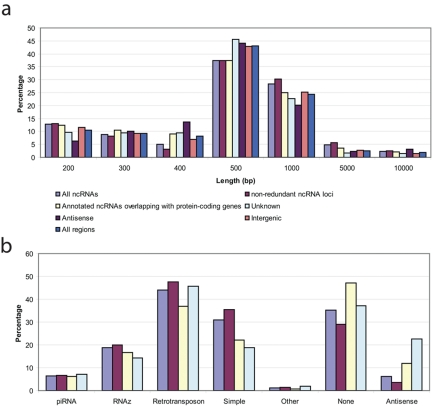
FIG 4 .
Characteristics of genomic regions differentially expressed during SARS-CoV infection. (a) The length distribution of genomic regions differentially expressed during SARS-CoV infection. The genomic regions are indicated below the graph as follows: All ncRNAs, 429 genomic regions that overlapped with one or more annotated ncRNAs; non-redundant ncRNA loci, 285 of 429 genomic regions that overlapped with the nonredundant set of 10,986 annotated ncRNAs as compiled in this study; Annotated ncRNAs overlapping with protein-coding genes, 144 of 429 genomic regions that overlapped with those annotated ncRNAs that we filtered out because of partial overlapping with a protein-coding gene (see Materials and Methods); Unknown, 977 genomic regions without any overlapping annotated genes; Antisense, 249 genomic regions that were antisense to annotated protein-coding genes; Intergenic, 1,157 genomic regions were located between annotated protein-coding genes; All regions, all 1,406 genomic regions identified. (b) Characteristics of genomic regions differentially expressed during SARS-CoV infection. The genome regions are depicted as in panel a. Annotations showing what the identified genomic regions overlap with are shown below the x axis as follows: piRNA, piwi-associated small RNAs; RNAz, conserved RNA secondary structures predicted by RNAz; Retrotransposon, retrotransposons of the SINE, LINE, LTR, and DNA superfamilies; Simple, simple repeats and low complexity; Other, remaining retrotransposons and repeats; None, no overlapping with the annotation categories above; Antisense, antisense to protein-coding genes annotated by UCSC or Ensembl. See text and Materials and Methods for details.