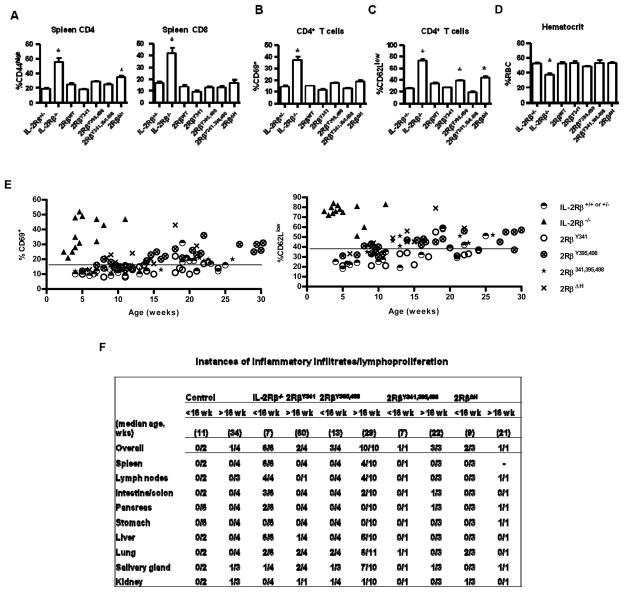
Figure 2. Autoimmune status of transgenic IL-2Rβ−/− mice expressing mutant IL-2Rβ.
The indicated IL-2Rβ transgenic mice were assessed for peripheral T cells with an activated (A) CD44high, (B) CD69+, or (C) CD62Llow (C) phenotype or for (D) hemolytic anemia. Controls were IL-2Rβ+/− or IL-2Rβ−/− littermate mice. Data are mean ± SEM of ≥7 mice/group <16 wks of age, except for 2RβWT (n=3) (A-C) and representative of at least 5 mice/group in (D). Autoimmune status was also assessed as a function of age for the indicated transgenic mice by enumerating (E) the % of CD4+ T cells that were CD69+ or CD62Llow. The line in (E) represents the value for two standard deviations above of the mean for littermate control mice. (F) Hematoxylin-eosin fixed sections of the indictaed tissues were examined for inflammatory infiltrates.