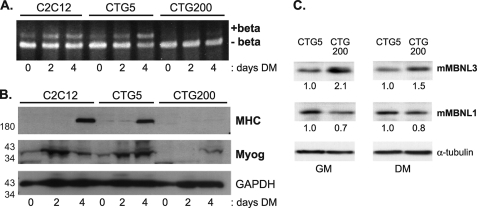
FIGURE 7.
Increased MBNL3 protein levels accompany defects in Mef2D β-exon splicing and muscle gene expression in a cell culture model for myotonic dystrophy. A, C2C12 clonal cell pools that express GFP fused to the full-length DMPK 3′-UTR containing either 5 (CTG5) or 200 (CTG200) CTG repeats were kindly provided by Dr. Mani Mahadevan. These cells and control C2C12 cells were exposed to differentiation conditions, and the splicing pattern of Mef2D was examined by RT-PCR and polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. B, expression of the muscle differentiation markers MHC and myogenin (Myog) were determined by Western blotting of whole cell lysates prepared from the indicated cell lines. GAPDH protein levels were monitored to control for total protein load. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kDa) are shown on the left. C, elevated levels of MBNL3 but not MBNL1 in C2C12 cells expressing CUG200 repeat transcripts. Whole cell lysates were prepared from C2C12 cells that expressed DMPK 3′-UTR containing either 5 (CTG5) or 200 (CTG200) CTG repeats. The cells were maintained in either growth (GM) or differentiation (DM) medium before the extracts were prepared. Approximately 100 μg of lysate was loaded onto SDS-polyacrylamide gels, transferred to nitrocellulose, and subjected to Western blotting with the MBNL3 mAb P1E7 and MBNL1 mAb MB1a. Tubulin levels were used to control for protein loading. The protein levels of MBNL3 and MBNL1 were determined using National Institutes of Health Image J software and used to calculate the relative levels, shown below each lane, under growth and differentiation medim conditions. The data presented were reproducibly observed in three independent experiments.