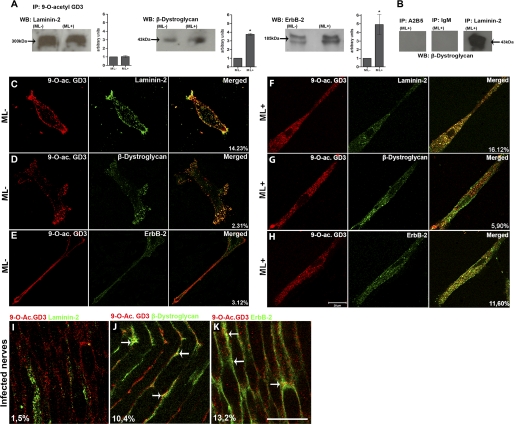
FIGURE 3.
9-O-Acetyl GD3 ganglioside associates with laminin-2, β-dystroglycan, and ErbB-2 receptor on the Schwann cell surface in vitro and in vivo. A, coimmunoprecipitation (IP) of 9-O-acetyl GD3 with laminin-2, β-dystroglycan, and ErbB-2 receptor in the absence (ML-) or presence (ML+) of M. leprae with histograms of quantitative analysis by densitometry for each protein analyzed by Western blotting (WB). B, as coimmunoprecipitation controls, anti-A2B5, mouse IgM isotype, and anti-laminin-2 were used, followed by Western blotting for β-dystroglycan. Control groups (ML-, n = 3) were normalized to 1 for comparison (ML+, n = 3). C–H, confocal sections of semi-confluent Schwann cells, uninfected (C–E) or after 48 h of ML exposure (F–H), double-immunolabeled for 9-O-acetyl GD3 and laminin-2 (C and F), β-dystroglycan (D and G), and ErbB-2 receptor (E and H). Right-hand columns (C–E and F–H) show merged images, where yellow dots represent colocalization. The percentages in C–E and F–H represent the degree of colocalization of 9-O-acetyl GD3 with laminin-2, β-dystroglycan, or ErbB-2 receptor in the presence or absence of ML. I–K, confocal longitudinal optical sections of NUDE mice sciatic nerves infected by M. leprae double-labeled for 9-O-acetyl GD3 and laminin-2, β-dystroglycan, or ErbB-2 receptor. Points of colocalization are indicated by arrows. The percentages in I–K represent the degree of colocalization. *, p < 0.01 (Mann-Whitney). n = 3 experiments for each ML ligand analyzed. Scale bars, C–K, 20 μm.