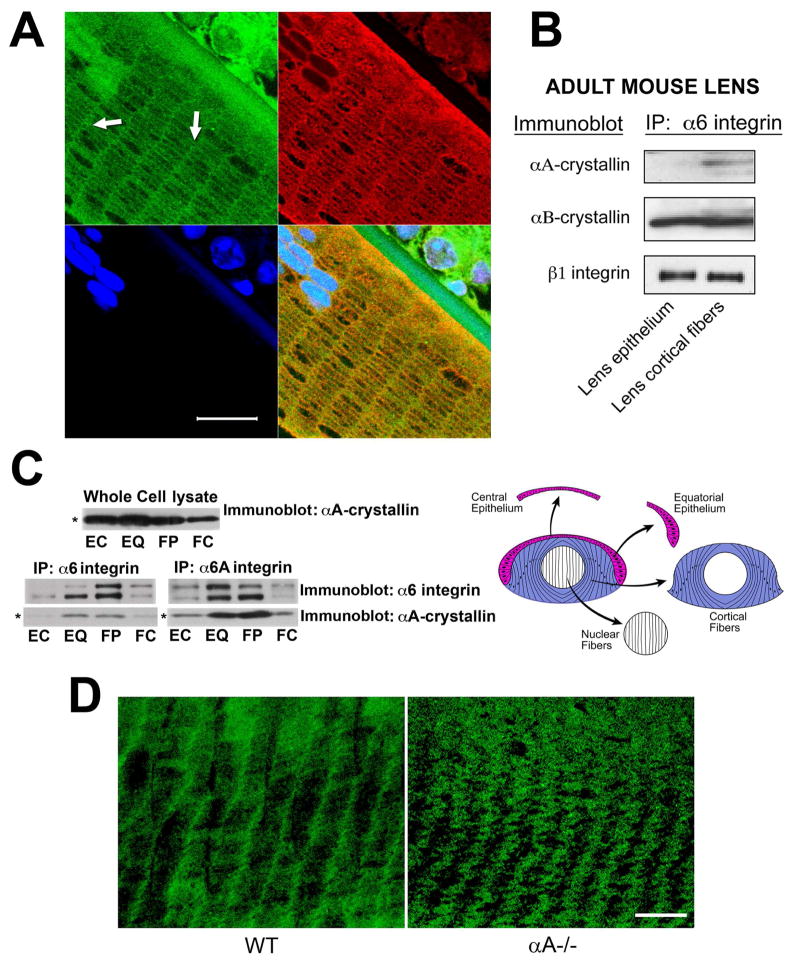
Figure 3.
Differentiation-state-specific association of αA-crystallin with α6 integrin complexes. (A) Confocal microscopic analysis of cross-sections of cortical lens fiber cells double labeled with antibodies to α6 integrin and αA-crystallin. α6 integrin localized all along the cell-cell interfaces of these hexagonally-packed cortical fiber cells, but was predominantly associated with the short arms of the hexagon. αA-crystallin was co-localized with α6 integrin along these lateral interfaces (white arrows). The green staining of nuclei at the top left of the image is due to non-specific staining with the α6 integrin antibody. DNA was stained with draq5(blue). Scale bar = 20 μm. (B) Adult mouse lenses were dissected into epithelial and cortical fiber fractions as diagrammed in Figure 2C. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated with an antibody to α6 integrin, and immunoblotted with antibodies to αA-crystallin, αB-crystallin, and ß1 integrin. Note that αA-crystallin association with α6 integrin was specific to cortical fiber cells, while the association of αB-crystallin with α6 integrin occurred in both lens epithelial and cortical fiber cells. (C) Chicken embryo lenses were dissected into four differentiation state-specific fractions: central epithelium (EC, red), equatorial epithelium (EQ, red), cortical fiber cells (FP, blue), and nuclear fiber cells (FC, white), as diagrammed in C. Cell extracts were immunoprecipitated either with an antibody to α6 integrin (recognizes both α6A and α6B integrin isoforms) or an antibody specific to α6A integrin, and immunoblotted with antibodies to αA-crystallin and α6 integrin. Note that the association of αA-crystallin with α6 integrin in these embryonic lenses was high in the zones of lens cell differentiation, including cells in the equatorial epithelium (EQ) and cortical fiber zones (FP). Note that the whole cell lysate (upper panel), had nearly equal levels of αA-crystallin in the central epithelium, equatorial epithelium and the cortical fiber cells. (D) Confocal microscopic analyses were performed on cortical fiber cells adjacent to the epithelium in wild-type (WT) and αA−/− lenses following immunostaining for α6 integrin. Note that α6 integrin was localized primarily to the short arms of these hexagonally packed fiber cells in wild-type lenses. While α6 integrin remained associated with the short arms of cortical fiber cells in αA−/− lenses, its linear organization at the plasma membrane was lost and these integrin junctions exhibited a wavy, disorganized pattern at the plasma membrane. Scale bar = 20 μm.