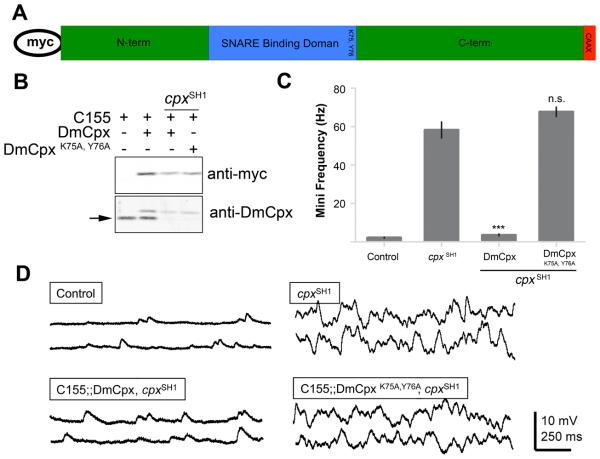
Figure 1.
DmCpx function as a fusion clamp requires the SNARE binding residues lysine 75 and tyrosine 76. (A) Schematic of Cpx protein domains. All transgenic lines generated in this study encoded a Cpx with an N-terminal myc tag. The SNARE binding domain is indicated in blue, and the localization of K75 and Y76 is shown. The C-terminal CAAX-box motif contained in some Cpx isoforms is shown in red. (B) The DmCpxK75A,Y76A transgenic protein is expressed at levels similar to the WT DmCpx transgenic protein and endogenous Cpx in lysates from adult transgenic heads. The top blot shows western probed with anti-myc antisera that recognizes the transgenic proteins driven by C155elav-Gal4 in WT or cpxSH1 background as indicated. The bottom blot is probed with anti-Drosophila Cpx antisera, which recognizes both endogenous and transgenic protein. Myc-tagged Cpx runs slower and can be separated from endogenous Cpx (indicated by the arrow). (C) Summary of mean mini frequency (Hz ± SEM). n = control (10), cpxSH1 (7), DmCpx (8), DmCpxK75A,Y76A (6). Statistical significance was determined by Student's t-test. (D) Sample traces of minis in control, cpxSH1, and rescue lines expressing WT DmCpx or DmCpxK75A,Y76A.