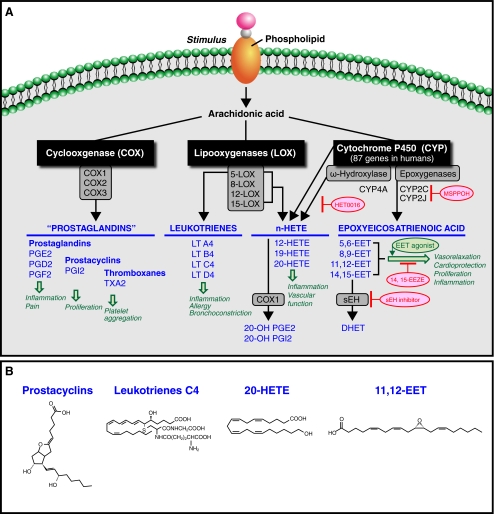
Fig. 1.
a, b Bioactive eicosanoids derived from the arachidonic acid cascade. Arachidonic acid is metabolized by three pathways—the cyclooxygenase (COX), lipoxygenase (LOX), and cytochrome P450 (CYP) pathways. Schematic overview of major mediators and their metabolites (blue); enzymes (black, boxed) and biological role (green). Inhibitors (red ovals) and agonists (green ovals). HETEs Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids, EETs epoxyeicosatrienoic acids, CYP cytochrome P450 enzymes. MS-PPOH is a selective inhibitor of a subset of epoxygenases. HET0016 is a selective inhibitor of the ω-hydroxlase CYP4A. The sEH inhibitor (soluble epoxide hydrolase inhibitor) increases EET levels by acting as an agonist of the EET pathway. 14,15-EEZE is a putative EET receptor antagonist. PGE 2 prostaglandin E2, PGI 2 prostacyclin, LTA 4 leukotriene A4, DHET dihydroxyeicosatrienoic acid, 20-OH PGE 2 20-hydroxy-prostaglandin E2