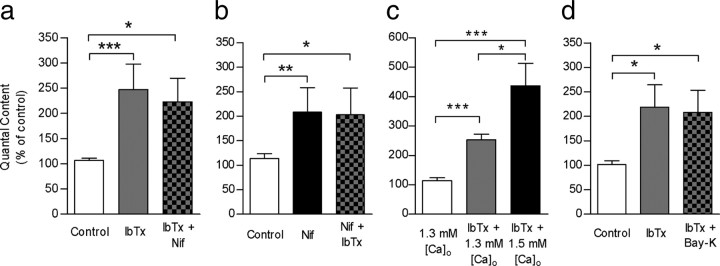
Figure 5.
L-type VGCC and BK channels are functionally coupled. a, Bar graph showing that the effects of 3 μm nifedipine on transmitter release were occluded by prior incubation of the cochlear preparation with 100 nm IbTx. b, Bar graph illustrating that the effects of 100 nm IbTx on transmitter release were occluded by prior incubation of the cochlear preparation with 3 μm nifedipine. c, Bar graph shows that elevating external Ca2+ from 1.3 mm to 1.5 mm increases transmitter release even in the presence of 100 nm IbTx, suggesting that the release “machinery” of this synapse is not completely saturated when BK channels are blocked. d, Bar graph showing that Bay-K was not able to reduce m if BK channels had been previously blocked by IbTx. Error bars are SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.