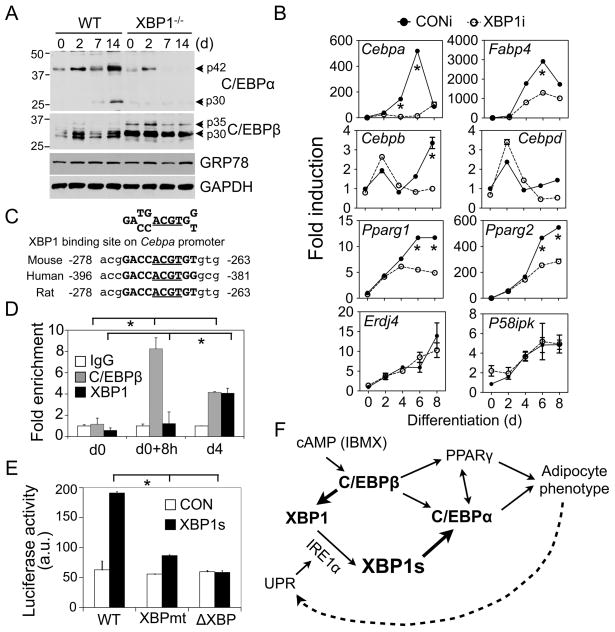
Figure 4.
XBP1 controls Cebpa expression. (A) Western blot analysis of C/EBPα and C/EBPβ protein levels in XBP1−/− and wildtype MEFs. GRP78 and GAPDH, loading controls. (B) Q-PCR analysis in differentiating 3T3-L1 expressing CONi and XBP1i #4. Data normalized to d0 time-point of 3T3-L1 CONi adipocytes. (C) Conservation of XBP1 binding sites on the Cebpa promoter. The core binding element ACGT is underlined. (D) ChIP analysis showing the recovery of Cebpa promoter from immunoprecipitates of C/EBPβ , XBP1 or control IgG prepared from 3T3-L1 cells at d0, 8 h postinduction and d4 as indicated. The amount of Cebpa promoter (−335 to −82 bp) recovered was quantitated using Q-PCR. Data normalized to the IgG controls at each point. (E) Luciferase assay showing effects of XBP1s on Cebpa reporter activity (−320 to +45 bp) in HEK293T cells transiently transfected with control GFP (CON) and XBP1s. The Cebpa reporter constructs with either mutation (XBPmt) or deletion (ΔXBP) of the XBP1 binding sites were included. Data represented as mean ± s.e.m.. *, P<0.05 using unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test comparing the samples included by the brackets. (F) Model showing the role of IRE1α-XBP1 in adipogenesis. The new findings described in this paper are highlighted in bold. See text for details.