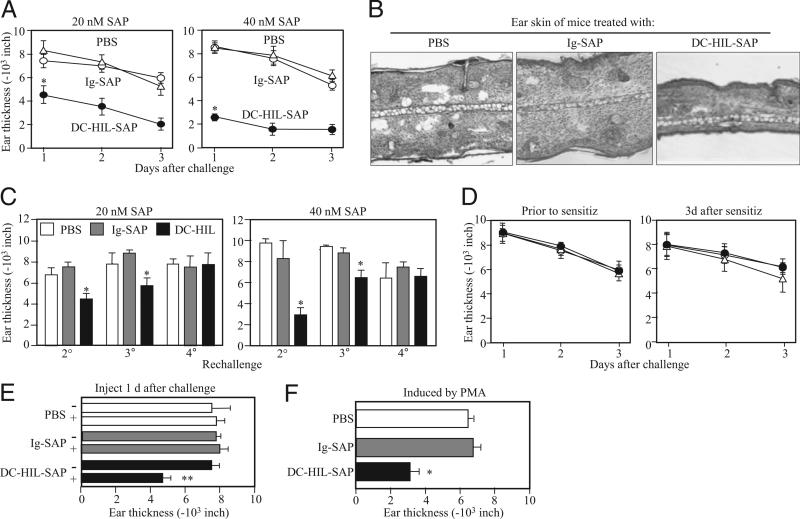
FIGURE 3.
Effects of DC-HIL-SAP on CH. On day 0, BALB/c mice (n = 4) were sensitized by painting 2% Ox on shaved abdominal skin. On day 6, CH was elicited in sensitized mice by painting 1% Ox or solvent control to right or left ears, respectively (Challenge). Ear thickness was measured daily from days 1–3 following challenge. A, Mice also were injected i.v. with PBS, Ig-SAP, or DC-HIL-SAP (20 or 40 nM) 3 h prechallenge. Daily change in ear thickness (10−3 inches) was plotted for each panel. B, On day 2, ear skin specimens of mouse representative in each group were stained with H&E and histologically examined under magnification ×10. C, These mice were kept for 1 wk and then rechallenged with Ox weekly for second (2°), third (3°) and fourth challenges (4°). Ear thickness was measured the day following challenge. D, In separate experiments, mice (n = 4) were also injected i.v. with the same SAP conjugates (40 nM) 3 h presensitization or 3 d postsensitization. E, One day postchallenge, mice (n = 4) were injected with PBS, Ig-SAP, or DC-HIL-SAP (40 nM). Ear thickness was measured just before (−) or 1 d after (+) injection. F, Similarly, mice (n = 4) were also sensitized and challenged but with a different chemical, PMA. Ear thickness was measured 1 d following challenge. Statistical significance is denoted by asterisks (*p < 0.001; **p = 0.003) as compared with ear thickness treated with control Ig-SAP. Data shown are representative of four (A) and two (B–F) independent experiments.