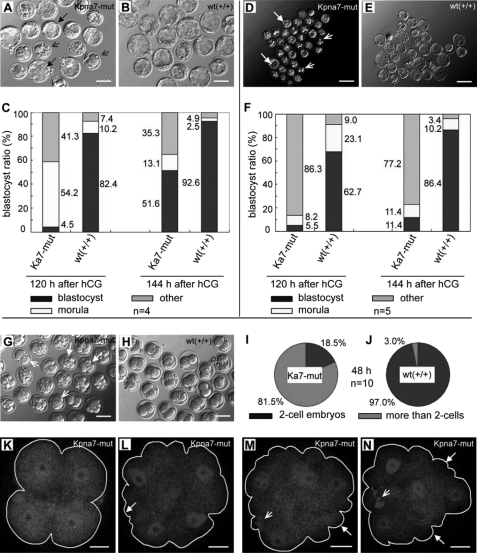
FIGURE 6.
Mutation of Kpna7-induced preimplantation developmental abnormalities in vitro. A–C, developmental abnormalities of naturally fertilized zygotes are induced in Kpna7 mutation mice. Many of the zygotes of Kpna7 group failed to develop into blastocyst stage (A). C, statistical analysis of preimplantation development 120 and 144 h after hCG injection. 48.4% of the Kpna7 mutation zygotes fail or are delayed from developing into blastocyst stage. D–F, parthenogenesis developmental abnormalities of naturally fertilized zygotes are induced in Kpna7 mutation mice. D and E, development of parthenogenesis one-cell embryos that collected from Kpna7 mutation and wild type mice. F, statistics analysis of parthenogenesis preimplantation development 120 and 144 h after hCG injection. Most (88.6) of the parthenogenesis one-cell embryos from Kpna7 mutation mice failed to develop into blastocyst stage. G–N, cell cycle is loss of control in parthenogenesis embryos of mutation mice after activation. G and H show embryos 48 h after hCG injection in Kpna7 mutation and wild type group (solid arrow, embryo containing four cells; open arrows, embryos containing two cells). I and J show statistics analysis of two-cell embryos and non-two-cell embryos 48 h after hCG injection in Kpna7 mutation group (I) and wild type group (J), respectively. K–N show four-cell embryos from Kpna7 mice with different morphological styles that observed 22 h after activation (48 h after hCG injection). The embryos are stained with CDC25 (solid arrows, abnormal morphology; open arrows, polar body DNA; bars, A, B, G, and H, 100 μm; D and E, 200 μm; K–N, 20 μm).