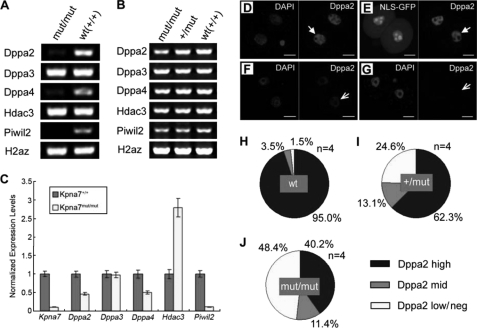
FIGURE 7.
Mutation of Kpna7 caused down-regulation of a set of chromatin remodeling factors. A and B, qualitative RT-PCR analysis shows that Kpna7 mutation induces down-regulation of dppa2, dppa4, and piwil2 in late two-cell embryos in Kpna7 mutation mice. C, real time RT-PCR analysis also shows that dppa2, dppa4, and piwil2 but not dppa3 are dramatically down-regulated in Kpna7 mutation group. hdac3 mRNA level is up-regulated. D–G, immunostaining analysis of DPPA2 protein levels in late two-cell stage embryos. Arrows indicate the DPPA2 signal (red). D and E show embryos injected with enhanced EGFP and NLS-EGFP, respectively. The DPPA2 signal is high in both wild type (D, solid arrow) and NLS-EGFP-injected late two-cell embryos (E, solid arrow). F and G, typical results of embryos derived from Kpna7 mutation mice. The DPPA2 signal is dramatically down-regulated (F, open arrow) or even hardly detected (G, open arrow) in late two-cell stage embryos. H–J, statistical analysis of DPPA2 staining intensities in late two-cell embryos. H–J show the results of wild type (H), Kpna7 heterozygous (I), and homozygous mutation mice (J), respectively. (Bars, 20 μm.)