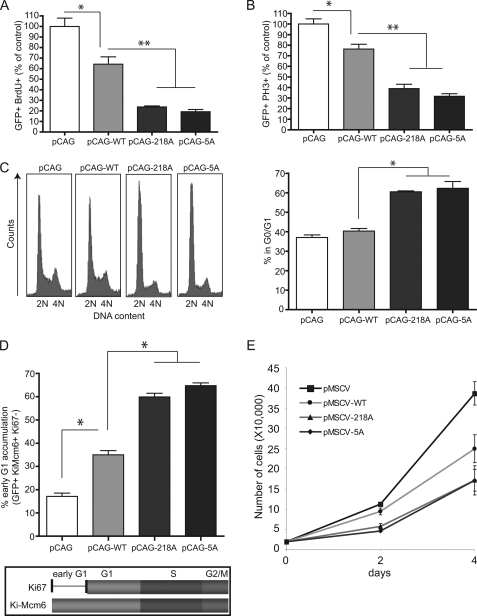
FIGURE 5.
Stabilized ATF4 induces an early G1 cell cycle arrest. A, NIH3T3 cells were transfected with the indicated pCAG-IRES-GFP plasmids for 48 h. Cells were given a 20 μm BrdU pulse for the last hour, fixed with antibodies against GFP and BrdU. Presented is the percentage of GFP and BrdU double positive cells. BrdU incorporation for the control (pCAG) was set to 100% and other samples were normalized to the control. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.001 (one-way analysis of variance). B, NIH3T3 cells were transfected as in A. Mitotic cells were analyzed by costaining with antibodies against GFP and phospho-histone H3 antibodies. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.01; **, p < 0.001 (one-way analysis of variance). C, FACS analysis of HeLa cells transfected with the indicated plasmids. GFP-positive cells were gated and analyzed for DNA content. Below, quantification of the percent of G0/G1 cells from C. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.001 (one-way analysis of variance). D, NIH3T3 cells were transfected with the indicated plasmids and stained with Ki-Mcm6 and Ki-67 antibodies. Early G1 arrest is calculated as the ratio of GFP + Ki-Mcm6 + Ki67, to total GFP + Ki-Mcm6 + cells. Data are presented as the mean ± S.E. (n = 3). *, p < 0.001 (one-way analysis of variance). E, NIH3T3 cells infected with retrovirus encoding the indicated variants of ATF4 were selected by puromycin for 3 days. Cells were replated at 20,000 cells per well, and cell number was counted over the course of 4 days.