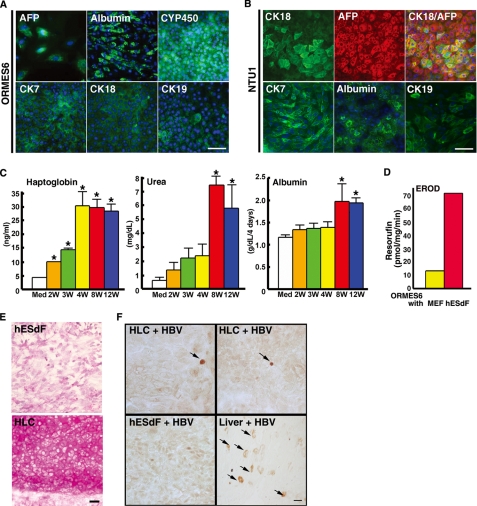
FIGURE 4.
The HLCs derived from primate ESCs co-cultured with hESdFs exhibited mature and functional phenotypes of hepatocytes. A and B, ICC analysis of hepatocyte marker expression in human (NTU1) and monkey (ORMES-6) ESC-derived HLCs showed that the majority of the HLCs were positively stained by the indicated hepatic markers. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 25 μm. C, temporal production of haptoglobin, albumin, and urea hepatocyte proteins during differentiation and maturation of monkey ESC-derived HLCs under hESdF co-culture conditions. The production of haptoglobin, albumin, and urea in the medium of differentiated cells increased in parallel with differentiation duration (Med, medium; 2W, 2 weeks; 4W, 4 weeks; 8W, 8 weeks; 12W, 12 weeks). The data correspond to the averages and S.D. of triplicate experiments, except the albumin data, which were the averages of four independent experiments. Significant differences between each time point and media are labeled (*, p < 0.05). D, ethoxyresorufin-O-deethylase assay showed that differentiated cells had a higher activity than control cells. E, periodic acid-Schiff staining showed glycogen storage in HLCs (lower panel), whereas the hESdF feeder cells were negative. F, immunoperoxidase staining showed positive nuclear staining of HBcAg (arrows, upper panels) in monkey ESC-derived HLCs infected with serum from patients with HBV infection for 3 days. The feeder cells (left lower panel) were negative. An HBV-infected liver section (right lower panel), stained for both cytoplasmic and nuclear (arrows); HBcAg was the positive control. Scale bar, 25 μm.