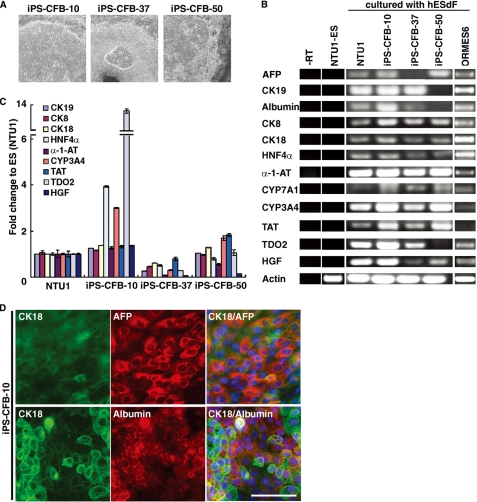
FIGURE 5.
Derivation of human iPSCs and characterization of iPSC-derived HLCs under hESdF co-culture conditions. A, phase contrast images of three human iPSC lines (cell lines 10, 37, and 50), which showed characteristic hepatocyte-like morphology after 3 weeks co-culture with feeder hESdFs. B, RT-PCR analysis of hepatic markers (CK8, CK18, CK19, AFP, Albumin, HNF4α, α-1-AT, CYP3A4, CYP7A1, TAT, TDO2, and HGF) expression in the HLCs derived from human ESCs (NTU1) and monkey ESCs (ORMES6) and three different iPSC clones, and in control ESCs (NTU1) without differentiation. C, QRT-PCR analysis of total RNA isolated from HLCs derived from iPSC-CFB-10, -37, and -50 clones for CK8, CK18, CK19, HNF4α, α-1-AT, CYP3A4, TAT, TDO2, and HGF expression. For each sample, relative expression levels were normalized to corresponding levels in human ESCs (NTU1). The data correspond to the averages and standard deviations of triplicate experiments. D, ICC analysis of hepatocyte markers in human iPSC-derived HLCs. HLCs derived from iPSC-CFB-10 clone at day 15 of differentiation were double-stained with anti-human CK18 (green) and AFP (red) or albumin (red) as indicated. The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar, 25 μm.