FIGURE 1.
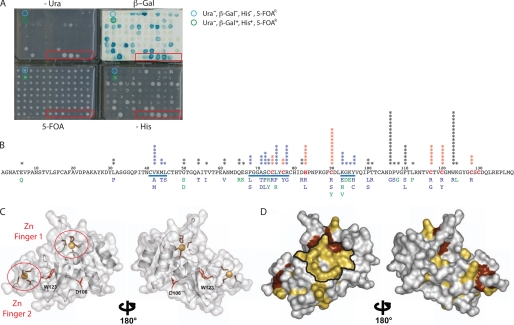
Identification of nsp10 IDAs unable to interact with nsp16 in RY2H. A, phenotypic assays were performed with clones isolated from the RY2H screen in a 96-well plate format using a semiautomated protocol (-Leu-Trp-His + 25 mm 3-AT, SC-Leu-Trp + 0.2% 5-FOA and SC-Leu-Trp-Ura and β-galactosidase activity) (45). Seven controls of known phenotypes were included (red box). B, mutations within positive clones from RY2H screen were identified by sequencing and reported on the nsp10 sequence. The stars indicate the number of times the mutated alleles were isolated. Stars in blue represent residues that are within the delineated potential surface of interaction. Mutants in blue are Ura−, β-Gal−, His−, and 5-fluorootic acid-resistant, and mutants in green are Ura−, β-Gal−/+, His−/+, and 5FOAR. Cysteine and histidine residues involved in chelating the zinc are in red. The underlined sequences represent groups of mutated amino acids exposed on the protein surface. C, ribbon representation of the monomeric nsp10 backbone structure (Protein Data Bank code 2FYG). Residues involved in zinc chelation are circled in red. Residues Asp106 and Trp123 are not exposed on the protein surface, as shown in a red stick representation on the nsp10 backbone. D, all mutations corresponding to IDAs identified by the RY2H screen are highlighted in yellow on the surface of nsp10 (Protein Data Bank code 2FYG). The zinc finger residues are shown in dark red, and the potential surface of interaction between nsp10 and nsp16 is delineated in black.