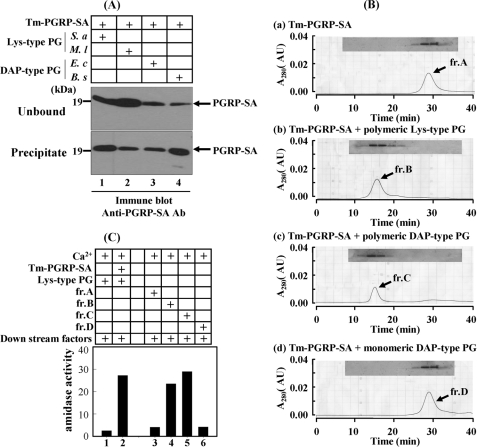
FIGURE 1.
Polymeric DAP-type PG forms a complex with PGRP-SA and induces activation of SPE zymogen. A, the ability of Tenebrio PGRP-SA to bind to polymeric Lys-type and DAP-type PGs. Lanes 1 and 2, Tenebrio PGRP-SA with S. aureus and M. luteus Lys-type PGs, respectively. Lanes 3 and 4, PGRP-SA with E. coli and B. subtilis polymeric DAP-type PGs, respectively. Tenebrio PGRP-SA supernatant and precipitate were analyzed by SDS-PAGE. B, elution patterns of gel filtration column after loading Tenebrio PGRP-SA only (panel a), PGRP-SA with polymeric Lys-type PG (panel b), PGRP-SA with polymeric DAP-type PG (panel c), and PGRP-SA with lysozyme-treated monomeric DAP-type PG (panel d). The boxes indicate the SDS/PAGE analyses patterns of the fractions after column. C, measurement of amidase activity of activated SPE. Lane 2, a mixture of Lys-type PG with PGRP-SA and downstream factors (GNBP1, MSP, SAE, and SPE zymogens). Lanes 3–6 indicate the amidase activities of a mixture of fractions A–D in Fig. 6B with downstream factors in the presence of Ca2+. Tm, T. molitor.