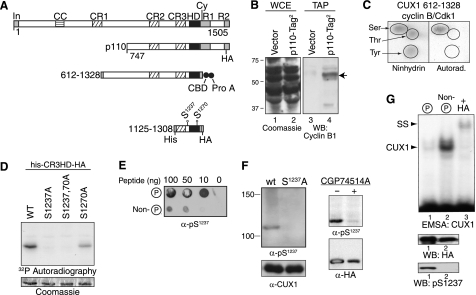
FIGURE 3.
Cyclin B/CDK1 phosphorylates CUX1 on serines 1237 and 1270. A, diagrammatic representation of CUX1 and the recombinant proteins used to investigate phosphorylation by cyclin B/CDK1. Shown at the top are the functional domains and the cyclin-interacting motif. In, inhibitory domain; CC, coiled-coil; CR1, CR2, and CR3, cut repeats 1, 2, and 3; HD, cut homeodomain; Cy, cyclin-binding motif. Epitope tags are as follows: CBD, calmodulin binding domain; Prot A, protein A; His, histidine tag; HA, hemagglutinin. B, interaction between p110 CUX1 and cyclin B1 was investigated in cells expressing a recombinant p110 CUX1 protein with two tags at its C terminus, p110-Tag2. Whole cell extracts (WCE) were separated by SDS-PAGE and stained with Coomassie Blue (left panel) or were submitted to tandem affinity purification and analyzed by immunoblotting using a cyclin B1 antibody (right). As a control, the same procedures were performed using cells carrying the empty vector (vector). C, recombinant His-tagged CUX1 protein containing amino acids 612–1328 was purified from bacteria and then phosphorylated in vitro using [γ-32P]ATP and a preparation of cyclin B/CDK1 from Sf9 cells. Kinase reactions were subjected to acid hydrolysis, mixed with an excess of phosphoamino acid (serine, threonine, and tyrosine), and subjected to two-dimensional electrophoresis on TLC plates. The position of single amino acids was revealed with ninhydrin, and phosphorylated CUX1 amino acids were revealed by autoradiography. D, in vitro kinase assays in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP were performed using cyclin B/CDK1 from Sf9 cells and recombinant CUX1 proteins containing the cut repeat 3 and Cut homeodomain (CR3-HD), a histidine, and a hemagglutinin tag (his-CR3HD-HA, CUX1 amino acids 1125–1308) and carrying serine to alanine substitutions at residues 1237 and 1270, as indicated. Protein loading was verified by Coomassie Blue staining and phosphorylation, by autoradiography. E, rabbits were immunized with a phosphopeptide (Cys-YSQGApSPQPQHQ) corresponding to serine 1237 and its surrounding residues. Dot blot assays were performed to compare the affinity of unpurified bleeds for phospho- and nonphosphorylated peptides. F, immunoblotting was performed with purified anti-Ser(P)1237 and anti-CUX1 antibodies. Left, whole cell extracts from NMuMG cells stably expressing either wild type (wt) p110 CUX1 or p110S1237,1270A CUX1 (S1237A). Right, whole cell extracts from HEK293 cells transiently transfected with p110 CUX1-HA and treated or not for 16 h with the CDK1 inhibitor CGP74514A (20 μm). G, kinase assays were performed as detailed in C but with cold ATP. Phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated proteins were separated by affinity chromatography using the Qiagen phosphoprotein purification column and separated by SDS-PAGE. Phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated CUX1 proteins were analyzed by immunoblotting with an α-HA antibody and a phosphoserine 1237-specific antibody, and in EMSA using a using a radiolabeled CUX1 probe. The supershift (SS) in the presence of HA antibodies confirmed the identity of the CUX1 retarded complex (lane 3). WB, Western blot.