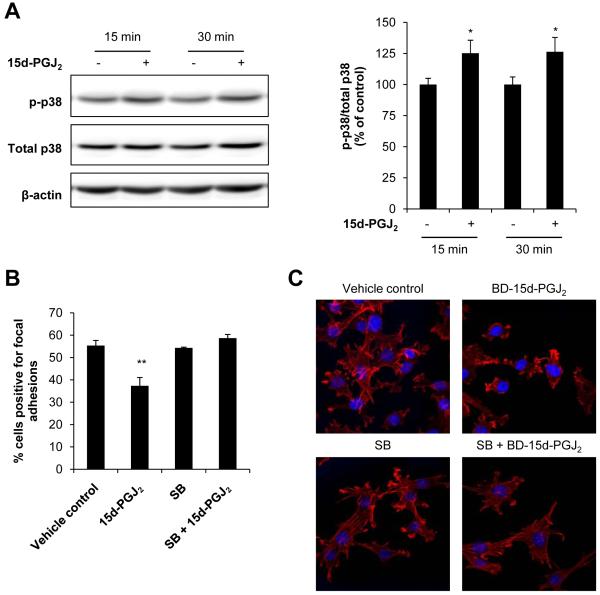
Figure 6. Role of p38 in focal adhesion disassembly and cytoskeletal arrangement regulation.
JC cells were treated with 15d-PGJ2 (0.3 μM, 15 and 30 min) or ethanol (EtOH) as a vehicle control and phosphorylated p38 (p-p38) was determined by Western blot analysis and quantified. A representative Western blot image is shown. Values represent the ratio of p-p38/total p38 normalized to time-matched vehicle control (A). JC cells were pretreated with the p38 inhibitor SB203580 (“SB”; 10 μM, 30 min), and then 15d-PGJ2 (0.3 μM) was added for an additional 4 h. Cells were fixed in 3% glutaraldehyde and focal adhesions quantified using interference reflection microscopy. Values represent the mean percentage of cells scored positive for focal adhesions (B). JC cells were also pretreated with SB (10 μM, 30 min), and then BD-15d-PGJ2 (0.24 μM) was added for an additional 30 min. Cells were then fixed, permeabilized and stained with 2 units of Alexa Fluor® 633 Phalloidin to visualize F-actin (red channel). Nuclei were visualized with DAPI (blue channel). Representative images of red and blue channel merged images are shown from samples prepared in triplicate. EtOH and DMSO were used as vehicle controls. (C). Values shown represent means ± SEM, n = at least 3-6. ** p < 0.01 compared to vehicle control.