Figure 2. Interaction between rhNPY genotype (T/T, T/G, G/G) and early rearing history (MR, mother- reared, vs. PR, peer-reared) on CSF levels of NPY.
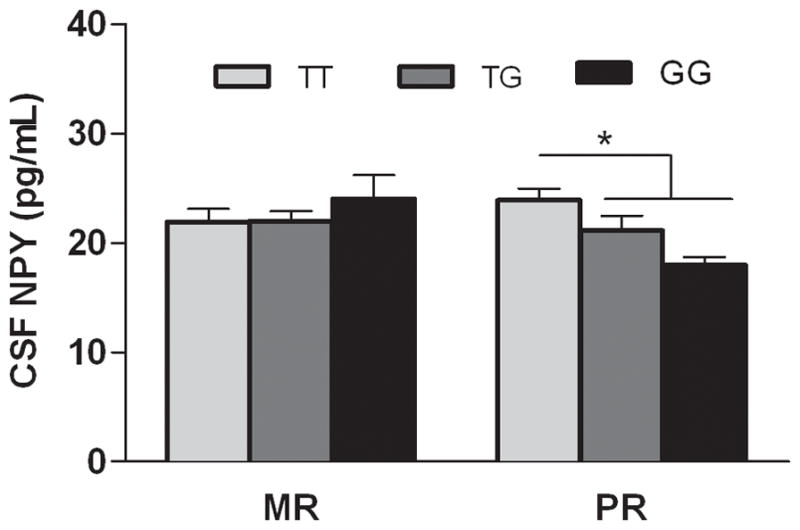
There was an interaction between genotype and rearing (F(2, 66) = 4.2, P < 0.02). The G allele dose-dependently decreased levels of NPY measured in a cisternal CSF sample among stress-exposed monkeys (Tukey-Kramer, P < 0.05) (MR T/T = 17, MR T/G = 14, MR G/G = 4; PR T/T = 16, PR T/G = 13, PR G/G = 8). Genotype accounted for 28 % of the variance in PR subjects. Values shown are mean pg/ml ± SEM. * P < 0.05.
